NOAA recently put together some time lapse satellite photography using photos taken every week for the last 25 years by polar orbiting satellites. It provides a stunning look at the true extent of the Arctic ice loss over just the last two and a half decades. The ice there was even thicker and larger in the 1950s than in the 1990s, much more so, according to data from shipping and Naval records.
The Arctic is warming at several times the rate as the rest of the planet. This has major consequences for many Northern Hemisphere weather systems and patterns, as we have witnessed here in America in recent winters. The Arctic Ice Cap has already shrunk enormously in extent and thickness. The northern glaciers in Alaska and Asia are melting faster. Greenland is melting faster and scientists have determined that it has lost 9 trillion tonnes of ice in the last century, with most of the loss in the last 30 years, adding to sea level rise.
This article explains it all pretty clearly and contains two short NOAA videos about the ice at the North Pole. Be sure to watch at least the first video showing the ice over time.
The Arctic Ice is melting faster than the global average
The Marshalltown
BY TAYLOR AUSTEN
12 JANUARY 2016

The climate change in the Arctic has been at least twice as fast as the global average. So Arctic Ocean ice levels are in decline.
Now, US scientists prepares a new time laps to show how large ice packs which survive more than one summer are becoming less frequent occurrences.
The areal extent, concentration and thickness of sea ice in the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas have strongly decreased during the recent decades, but cold, snow-rich winters have been common over mid-latitude land areas since 2005.
Each year sea ice in the Arctic Ocean builds up in the winter months and thin ice melts away during summer.
However, recently the change seems to be more dramatic. Old, multilayered icebergs are in decline and this visualization by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) makes everything clear related to how the Arctic is "warming faster than the global average."
Using satellite data, the video describes the decline of nine years or older ice packs from 1990 to 2015.
Sea ice in the Arctic can be characterized by areal extent, thickness, age, and movement.
The conditions on top of sea ice, such as the snow thickness and melt ponds, are alsoimportant. The oldest packs, shown in white, can be seen to deplete dramatically around 2008 amid the darkest blue seasonal ice.
According to the NOAA 2015 Arctic Report Card, last winter, - 'The spread of sea ice in the area was "the smallest on record" and the "melt season was 30 to 40 days longer than average" in the northern regions of Greenland'.
"Since the 1980s, the amount of multiyear ice has declined dramatically. In 1985, 20 percent of the ice pack was very old ice, but in March 2015 old ice only constituted three percent of the ice pack," it added.
The ice retreat is having an impact on wildlife, said the NOAA, changing the habitat for creatures such as walruses, who have to travel further for mating or birthing areas.
In September 2015, NASA reported that sea ice concentration was the fourth lowest on record since observations from space began.
Wowie Zowie. "Faster than the Global Average? " What's that?
The Arctic Ice is melting faster than the global average
That would be all of the Earth's ice.....all of the mountain glaciers and coastal glaciers, the Greenland ice sheets, the Antarctic ice sheets, plus the floating sea ice.
Nope! Your usual ignorant assumption.
And where is that? In the Arctic and Antarctic..
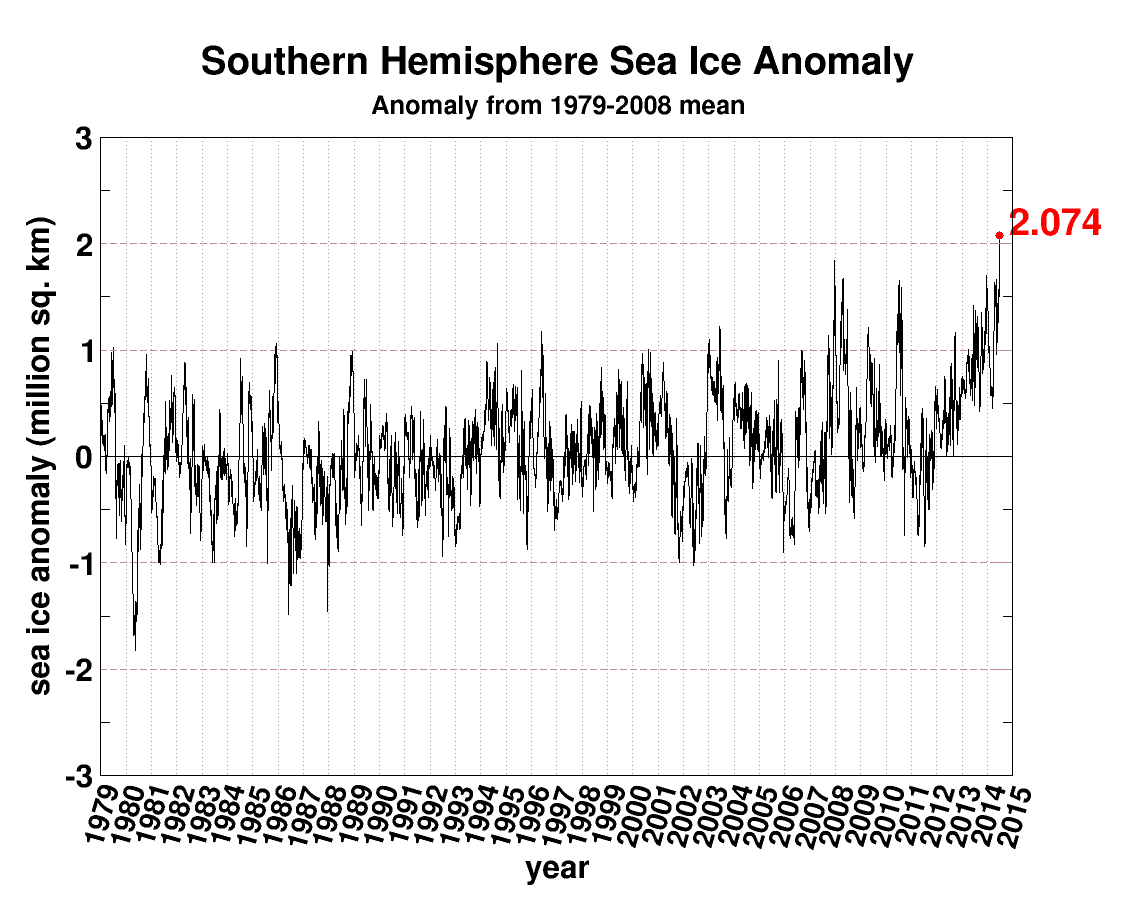
In the Antarctic, a thin fringe of seasonal floating sea ice that almost disappears at its minimum in the SH summer, surrounds a continent covered in miles thick ice sheets. When Antarctic sea ice is at its minimum and almost disappears, the enormously greater volume of land based ice is still there. In the Arctic, when the floating sea ice melts away, nothing is left but open ocean.
 Sea ice climatologies: Arctic and Antarctic sea ice concentration climatology from 1981-2010, at the approximate seasonal maximum and minimum levels based on passive microwave satellite data. Image provided by National Snow and Ice Data Center, University of Colorado, Boulder.
Sea ice climatologies: Arctic and Antarctic sea ice concentration climatology from 1981-2010, at the approximate seasonal maximum and minimum levels based on passive microwave satellite data. Image provided by National Snow and Ice Data Center, University of Colorado, Boulder.
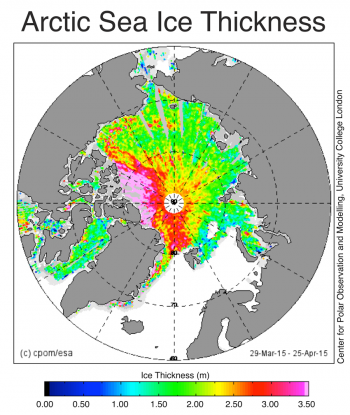
But more importantly TinkerBelle -- HOW THICK is "multi-year Arctic sea ice" ?? Pictures of 400Ft thick glaciers come to mind. But they are not "sea ice".. The multi year ice in the Arctic Ocean is about 2 to 8 ft thick.
Well, shit4brains, you're wrong. As usual.
State of the Cryosphere - Sea Ice
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC)
DECLINE IN ARCTIC SEA ICE EXTENT
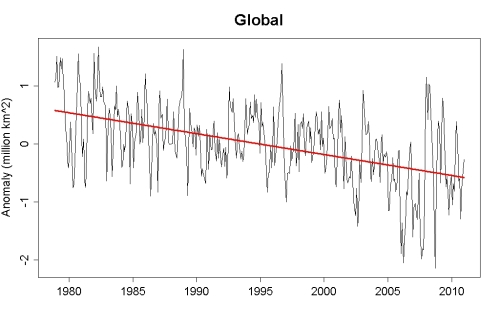
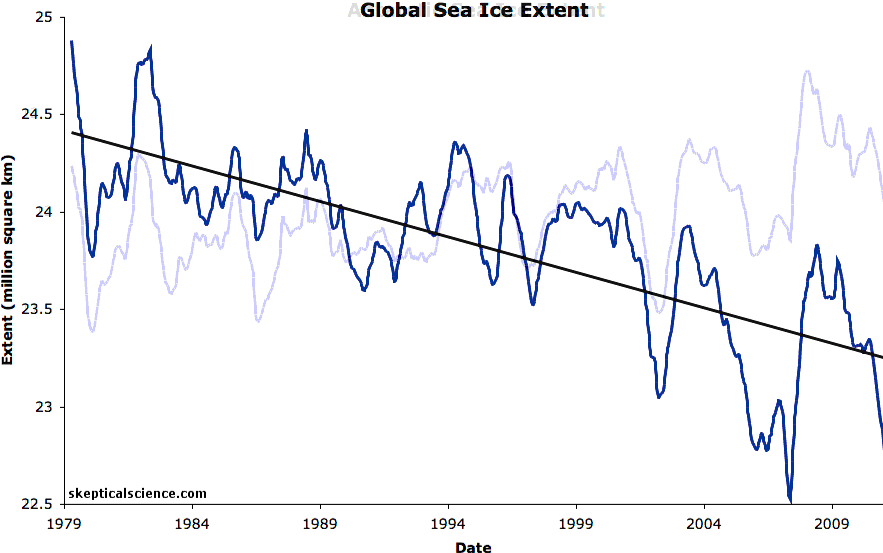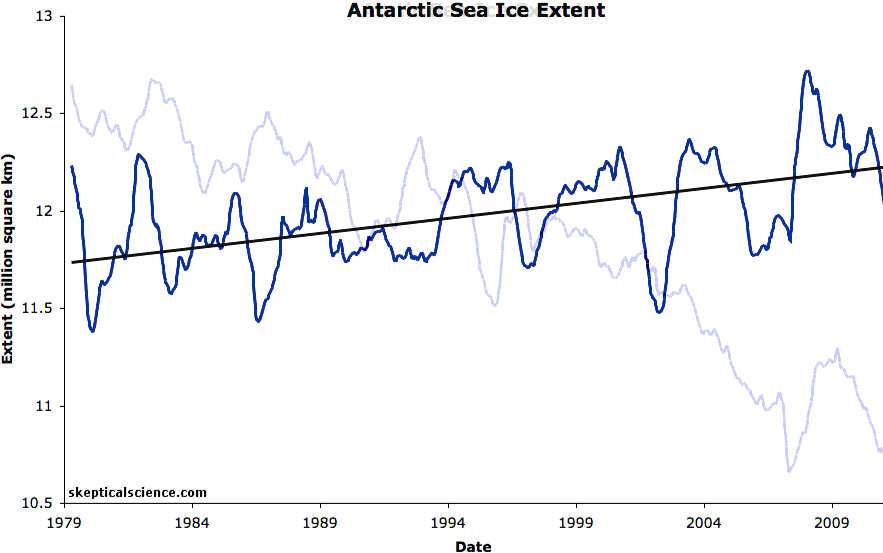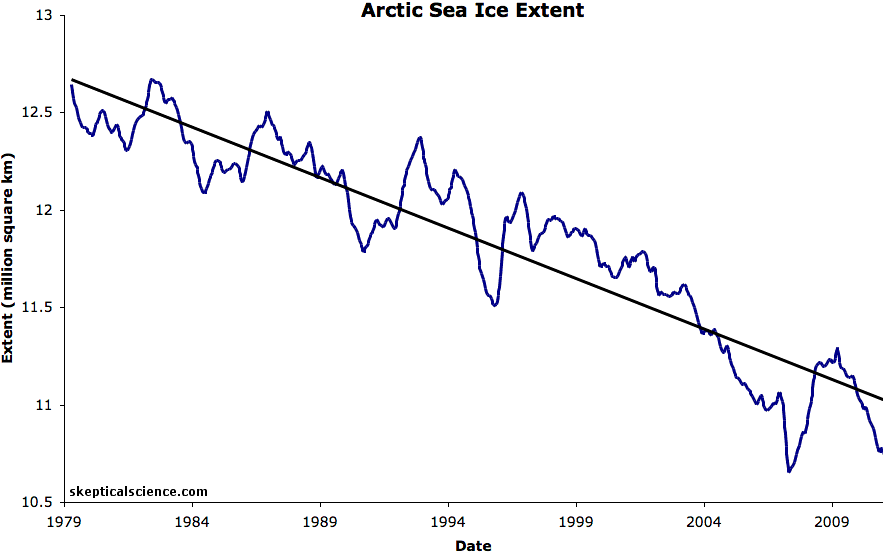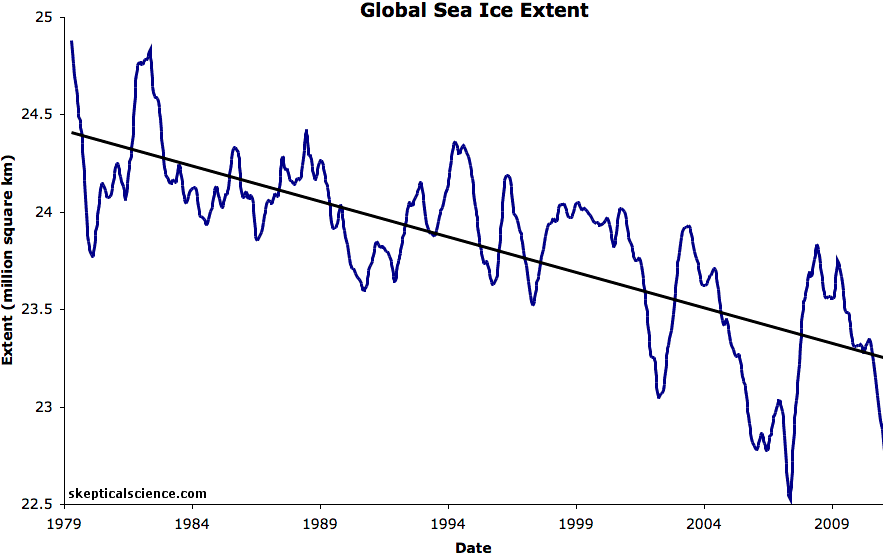
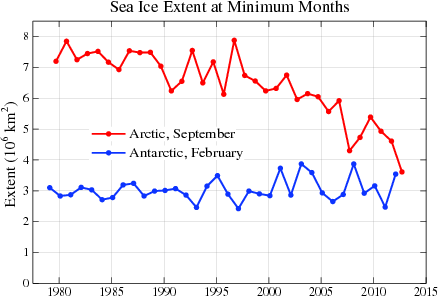
Passive microwave satellite data reveal that, since 1979, winter Arctic ice extent has decreased about 3 to 4 percent per decade (Meier et al. 2006). The Arctic sea ice September minimum extent reached a new record low in 2012 of 3.41 million square kilometers, 44 percent below the 1981-2010 average, and 16 percent below the previous record in 2007. Over the last 13 years, a new record was set four times (2002, 2005, 2007, and 2012) and several other years saw near-record lows, particularly 2008 and 2011. As NSIDC reported in October 2015, the nine lowest September ice extents over the satellite record have all occurred in the last nine years.
DECLINE IN ARCTIC SEA ICE THICKNESS
Sea ice thickness likewise showed substantial decline in the latter half of the 20th century (Rothrock et al. 1999). Using data from submarine cruises, Rothrock and collaborators determined that the mean ice draft (the ice extending below the water surface) at the end of the melt season in the Arctic decreased by about 1.3 meters between the 1950s and the 1990s.
Estimates based on measurements taken by NASA's ICESat laser altimeter, first-year ice that formed after the autumn of 2007 had a mean thickness of 1.6 meters. The ice formed relatively late in the autumn of 2007. NSIDC researchers had actually anticipated this first-year ice to be thinner, but it nearly equaled the thickness of 2006 and 2007. Snow accumulation on sea ice helps insulate the ice from frigid air overhead, so sparse snowfall during the winter of 2007-2008 might have actually accelerated the sea ice's growth.
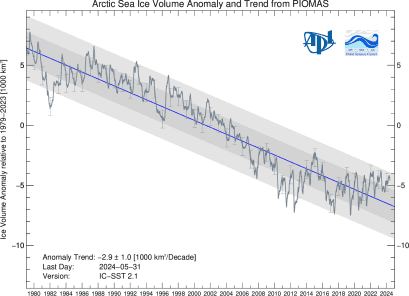
A recent study examined sea ice thickness records from submarines and ICESat observations from 1958 to 2008 (Kwok and Rothrock 2009). Examining 42 years of submarine records (1958 to 2000), and a five years of ICESat records (2003 to 2008), the authors determined that mean Arctic sea ice thickness declined from 3.64 meters in 1980 to 1.89 meters in 2008—a decline of 1.75 meters. A study published in 2013 compared sea ice volume between two periods: 2003-2008 and 2010-2012. The researchers used data from ICESat, the Pan-Arctic Ice-Ocean Modelling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS) and the European Space Agency CryoSat-2 mission, and found that sea ice volume declined by 4,291 cubic kilometers at the end of summer, and 1,479 cubic kilometers at the end of winter (Laxon et al. 2013). CryoSat-2 continues to monitor sea ice thickness as researchers refine study methods (Ricker et al. 2014).
Sea ice thickness and sea ice age are not the same thing, but sea ice age provides a proxy for thickness. A study published in 2007 found a dramatic change in the age of sea ice in the central Arctic Basin since the mid-1980s. In 1987, 57 percent of the ice pack was at least five years old, and a quarter of that ice was at least nine years old. By 2007, only 7 percent of the ice pack was at least five years old, and virtually none of the ice was at least nine years old (Maslanik et al, 2007). Multiyear ice coverage actually increased between March 2013 and March 2014, thanks to more ice surviving the summer melt season than had survived in the record-breaking summer of 2012. But overall, multiyear sea ice continues to decline in the Arctic (Perovich et al. 2014).
And at that thickness -- could be REGENERATED in a decade or so.. It is NOT a permanent condition even IF the multi year ice is now in decline..
You live in such a crackpot fantasy world, fecalhead.
The Earth is rapidly warming up and the Arctic is warming even faster. Scientists expect an essentially ice free Arctic within decades. Just how do you moronically imagine that the old thick Arctic ice is going to get magically "
REGENERATED"? Like EVER in our lifetimes, you poor sad imbecile, let alone "
in a decade or so"?
 )
)


 [/URL]
[/URL] )
)


 [/URL]
[/URL]