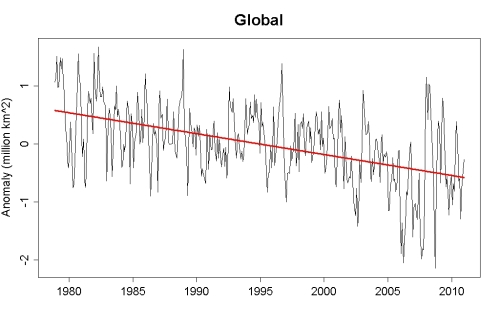
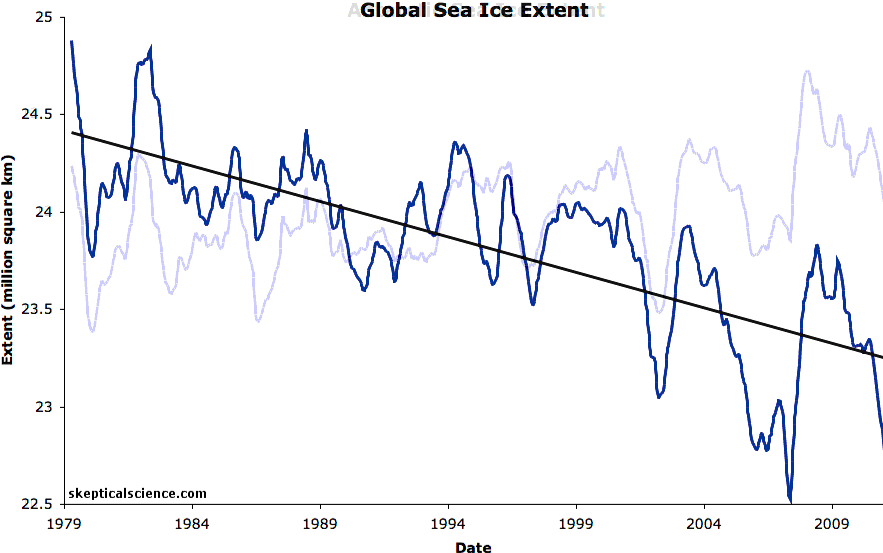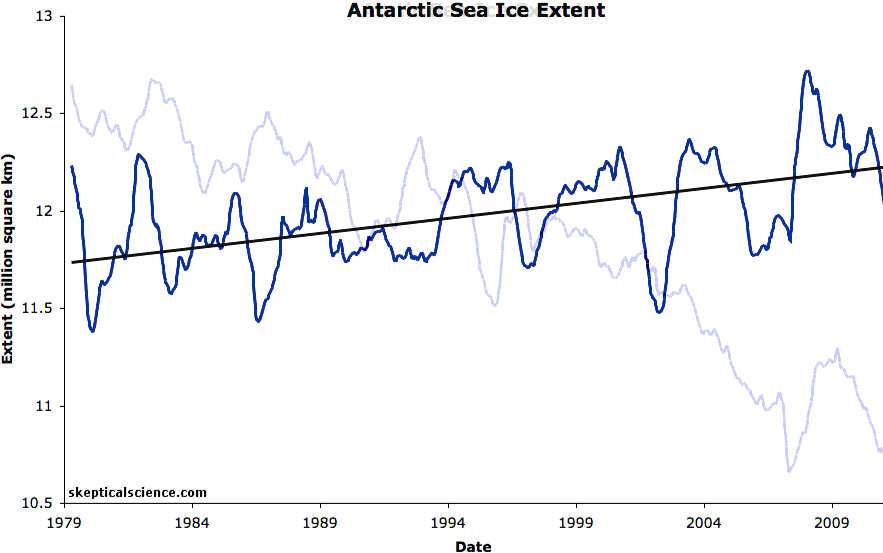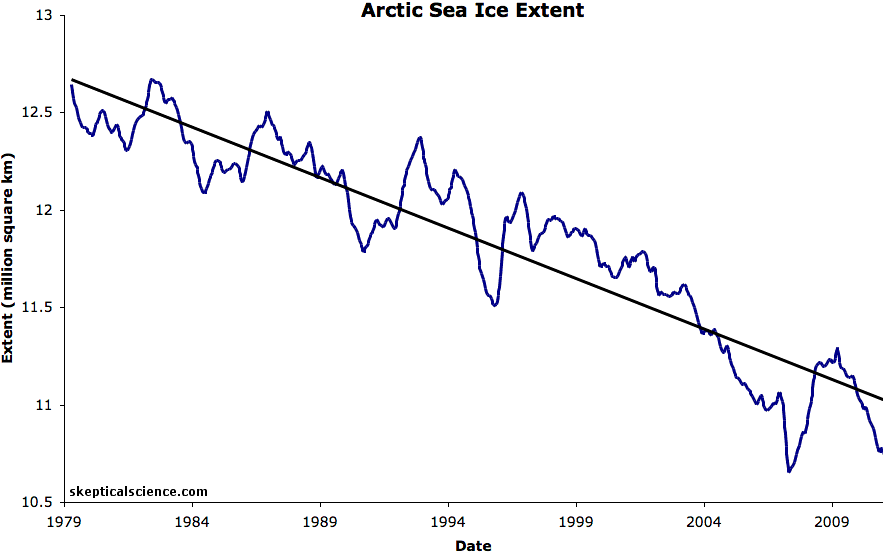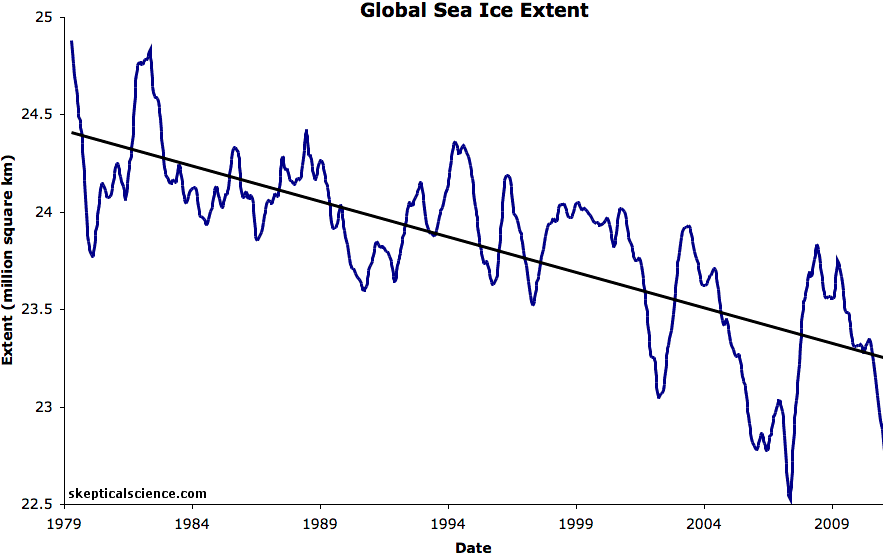
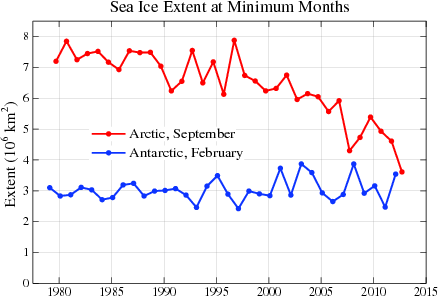
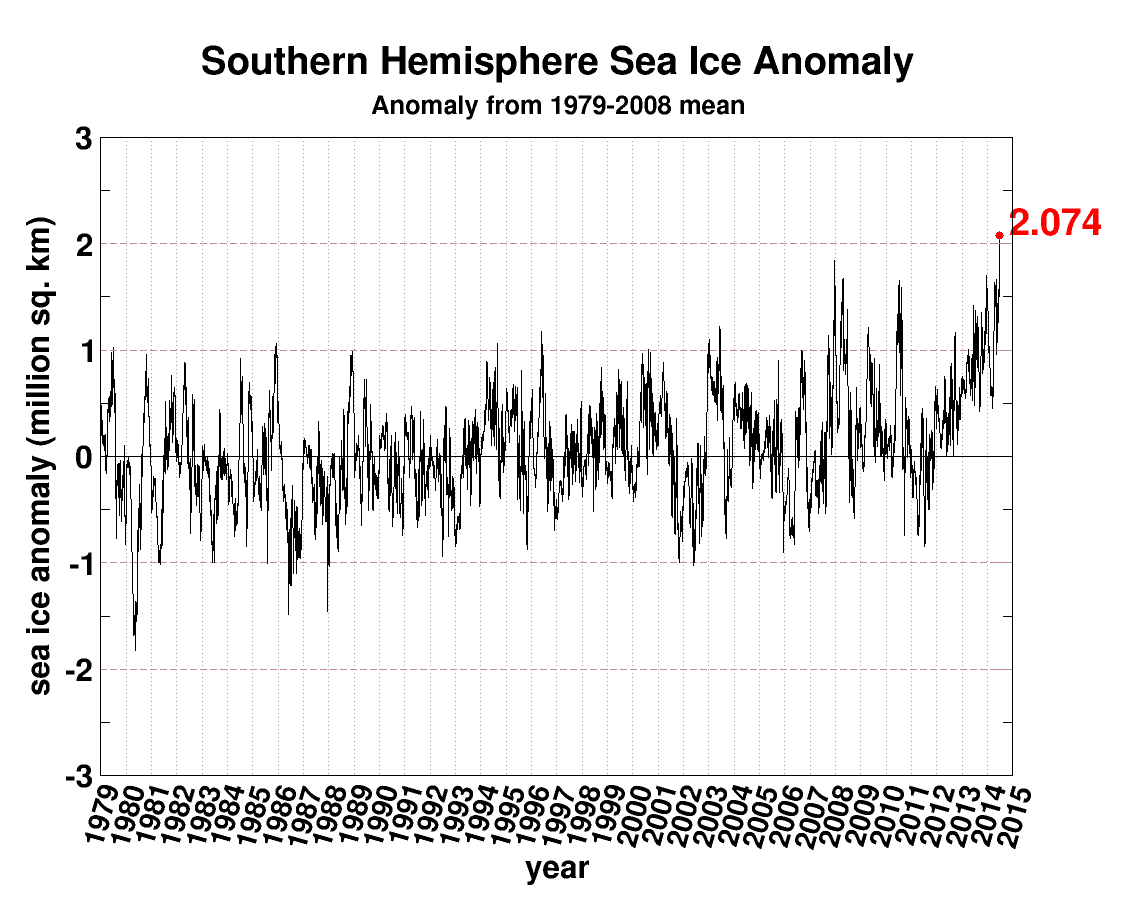
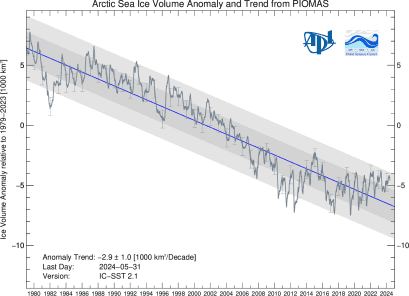
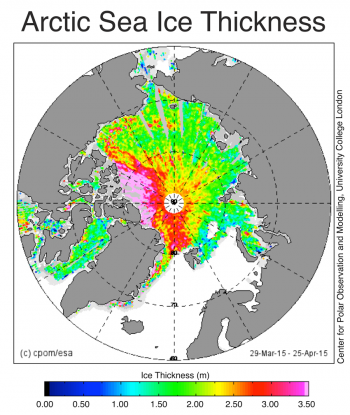
Thunders MO has been consistent for years on here. Disappears for weeks and then comes back with pronounced levels of anger and misery. Because his side is losing and his head explodes thinking about it.( lol....how many years have they been posting up pictures of glaciers in an effort to move the football a 1/2 yard to the goalposts 1,000 miles away??!!  )
)
Here we are 3 weeks out from Paris and nobody is caring.........its like it never happened. A gathering that needed to come away with agreement on trillions came away with agreement on a few billion. I cant stop laughing. Meanwhile, the rest of the world is worrying about 50 other things ahead of climate change = the science is mattering for dick. And this miserable jerkoff knows it too!!


[URL=http://s42.photobucket.com/user/baldaltima/media/football-field-gridiron-sports-poster-print.jpg.html] [/URL]
[/URL]
 )
)Here we are 3 weeks out from Paris and nobody is caring.........its like it never happened. A gathering that needed to come away with agreement on trillions came away with agreement on a few billion. I cant stop laughing. Meanwhile, the rest of the world is worrying about 50 other things ahead of climate change = the science is mattering for dick. And this miserable jerkoff knows it too!!



[URL=http://s42.photobucket.com/user/baldaltima/media/football-field-gridiron-sports-poster-print.jpg.html]
 [/URL]
[/URL]
Last edited: