Major greenhouse gases and sources
Carbon dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for
about three-quarters of emissions. It can linger in the atmosphere for
thousands of years. In 2018, carbon dioxide levels reached 411 parts per million at Hawaii's Mauna Loa Atmospheric Baseline Observatory, the
highest monthly average ever recorded. Carbon dioxide emissions mainly come from burning organic materials: coal, oil, gas, wood, and solid waste.
Carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas that drives global climate change, continues to rise every month. Find out the dangerous role it and other gases play.

www.nationalgeographic.com
According to observations by the NOAA Global Monitoring Lab, in 2021 carbon dioxide alone was responsible for about two-thirds of the
total heating influence of all human-produced greenhouse gases.
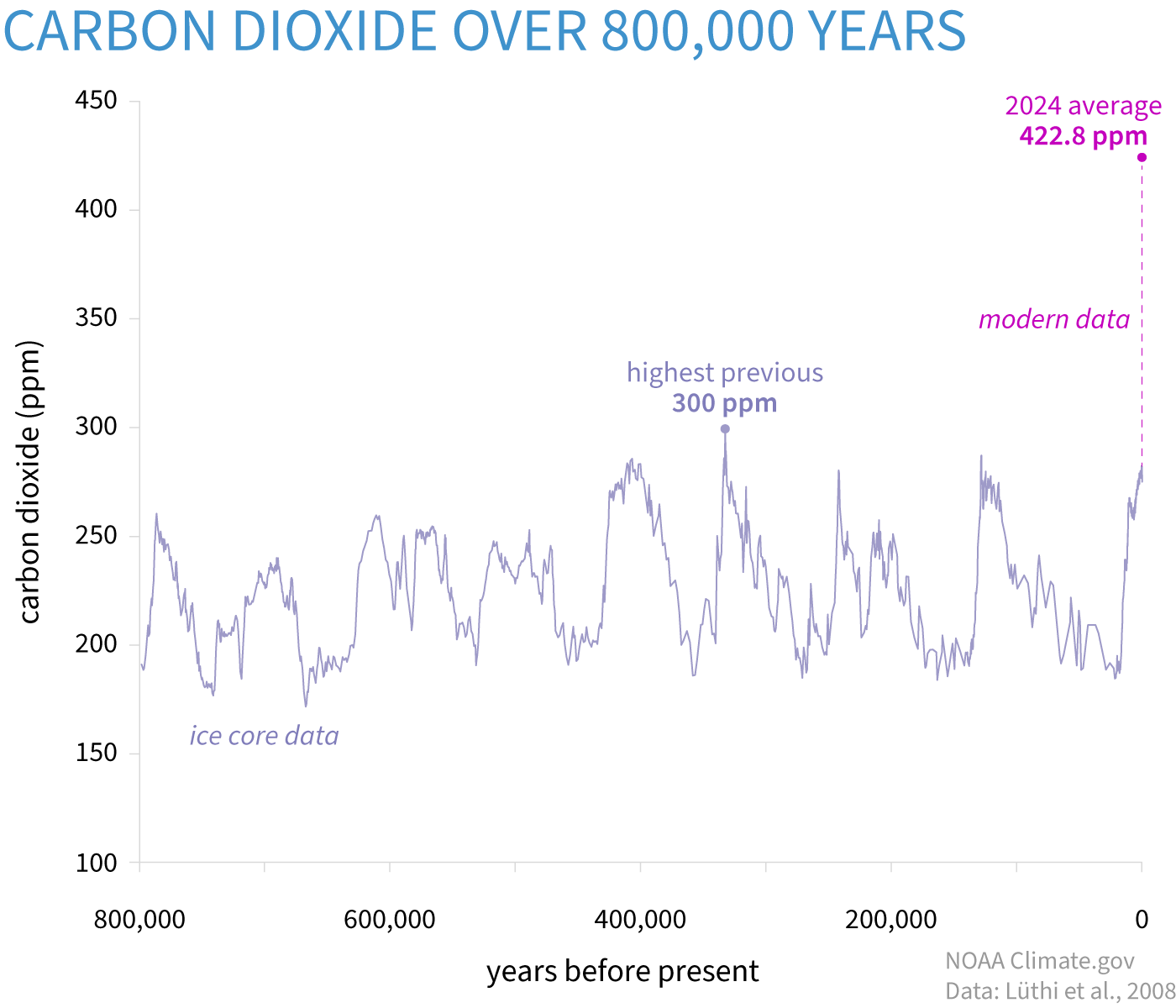
In the past 60 years, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased 100-200 times faster than it did during the end of the last ice age.

www.climate.gov
CO2 levels are now comparable to the Pliocene Climatic Optimum, between 4.1 and 4.5 million years ago, when they were close to, or above 400 ppm. During that time,
sea levels were between 5 and 25 meters higher than todayoffsite link, high enough to drown many of the world’s largest modern cities. Temperatures then averaged 7 degrees Fahrenheit higher than in pre-industrial times, and
studies indicateoffsite link that large forests occupied today’s Arctic tundra.