Old Rocks
Diamond Member
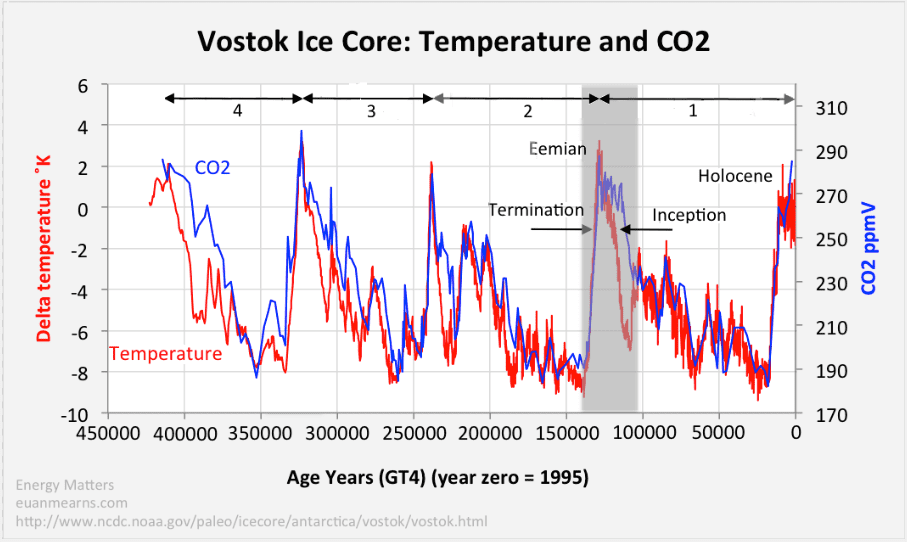
According to this study, it appears that the present CO2 level is the highest it has been since the Miocene.
Skip Nav Destination
RESEARCH ARTICLE| MAY 29, 2020
Brian A. Schubert;
A. Hope Jahren
Geology (2020) 48 (9): 888–892.
A 23 m.y. record of low atmospheric CO2 | Geology | GeoScienceWorld
Article history
 pubs.geoscienceworld.org
pubs.geoscienceworld.org
Skip Nav Destination
RESEARCH ARTICLE| MAY 29, 2020
A 23 m.y. record of low atmospheric CO2
Ying Cui;Brian A. Schubert;
A. Hope Jahren
Geology (2020) 48 (9): 888–892.
A 23 m.y. record of low atmospheric CO2 | Geology | GeoScienceWorld
Article history