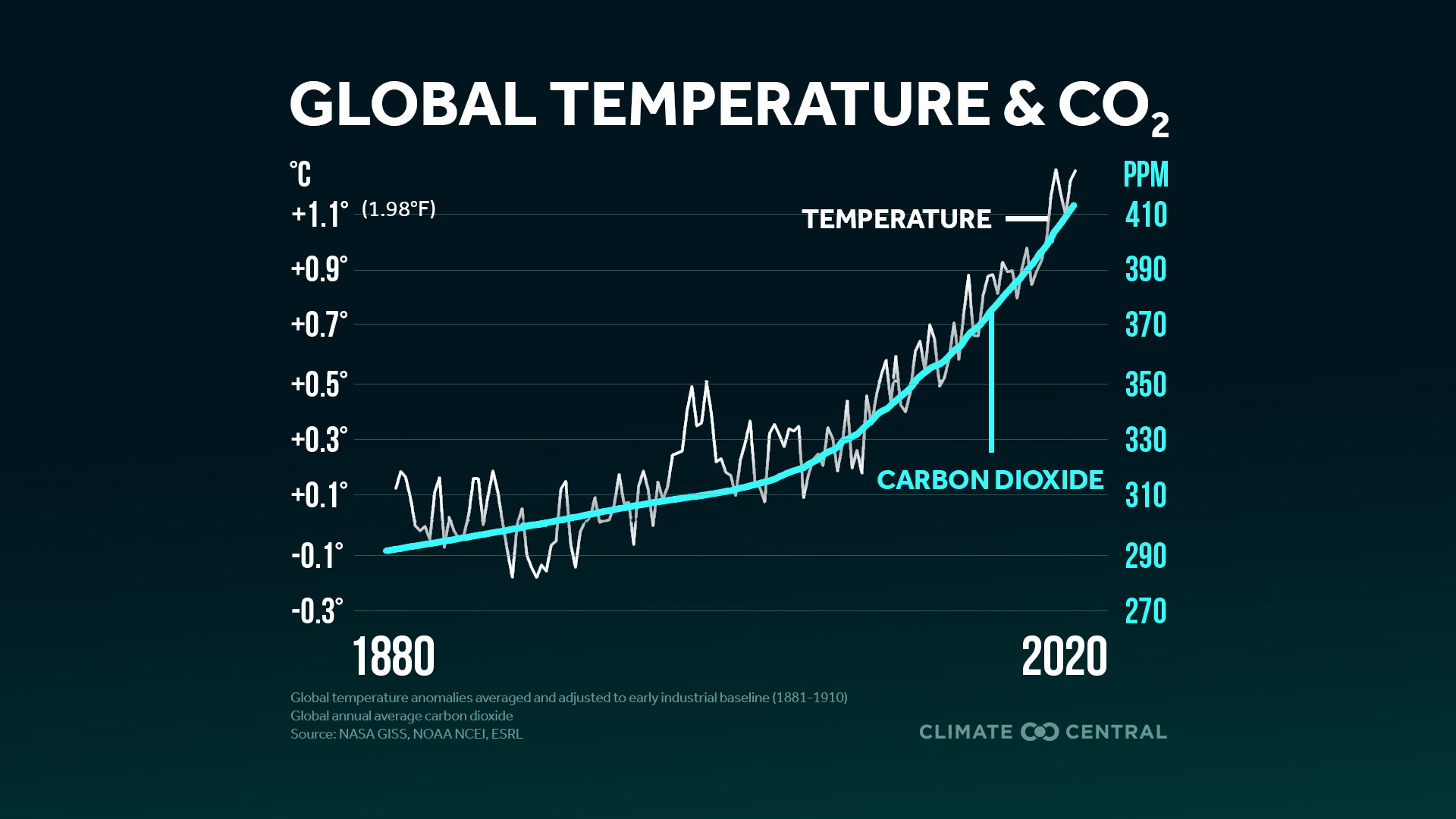
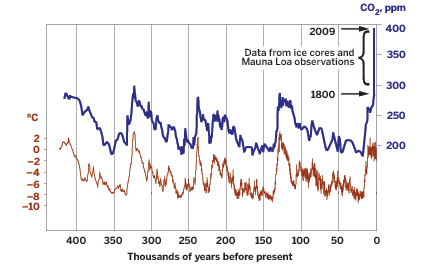
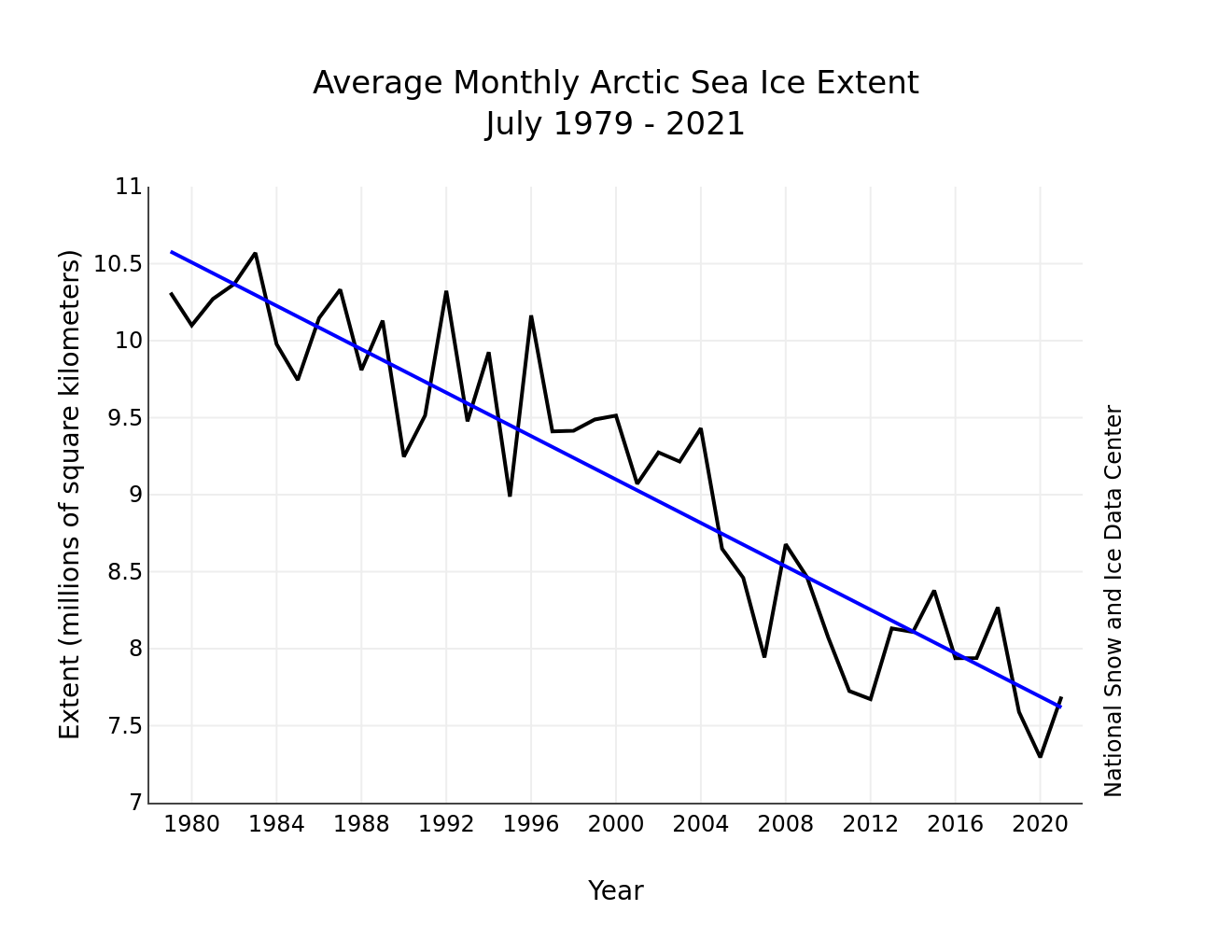
Yes, it is. Ice is melting in the Arctic, in Greenland, in Antarctica on land and sea and in glaciers around the planet. That ice is melting because the Earth's temperature is increasing. Earth's temperature is increasing because the greenhouse effect is being enhanced by human CO2 emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels in our automobiles and power plants.
If you have some other explanation for the world's ice melting, I would VERY much like to hear it.
No, I am not. I am reading and accepting mainstream studies conducted and published by scientists from all over the planet.
There have been five major ice ages and we are in one now.
Here is an informative discussion of ice ages I found from the Utah Geological Survey. It's only about a page long
What is an ice age?
An ice age is a long interval of time (millions to tens of millions of years) when global temperatures are relatively cold and large areas of the Earth are covered by continental ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Within an ice age are multiple shorter-term periods of warmer temperatures when glaciers retreat (called interglacials or interglacial cycles) and colder temperatures when glaciers advance (called glacials or glacial cycles).
At least five major ice ages have occurred throughout Earth’s history: the earliest was over 2 billion years ago, and the most recent one began approximately 3 million years ago and continues today (yes, we live in an ice age!). Currently, we are in a warm interglacial that began about 11,000 years ago. The last period of glaciation, which is often informally called the “Ice Age,” peaked about 20,000 years ago. At that time, the world was on average probably about 10°F (5°C) colder than today, and locally as much as 40°F (22°C) colder.
What causes an ice age and glacial-interglacial cycles?
Many factors contribute to climate variations, including changes in ocean and atmosphere circulation patterns, varying concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide, and even volcanic eruptions. The following discusses key factors in (1) initiating ice ages and (2) the timing of glacial-interglacial cycles.
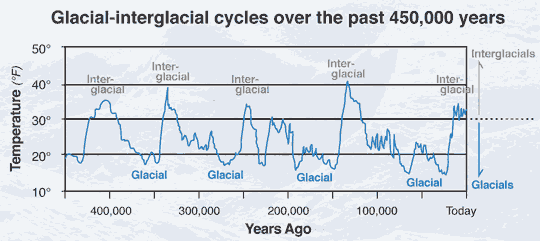
Four fairly regular glacial-interglacial cycles occurred during the past 450,000 years. The shorter interglacial cycles (10,000 to 30,000 years) were about as warm as present and alternated with much longer (70,000 to 90,000 years) glacial cycles substantially colder than present. Notice the longer time with jagged cooling events dropping into the colder glacials followed by the faster abrupt temperature swings to the warmer interglacials. This graph combines several ice-core records from Antarctica and is modified from several sources including Evidence for Warmer Interglacials in East Antarctic Ice Cores, 2009, L.C. Sime and others. Note the shorter time scale of 450,000 years compared to the previous figure, as well as the colder temperatures, which are latitude-specific (e.g., Antartica, Alaska, Greenland) temperature changes inferred from the Antarctic ice cores (and not global averages).
One significant trigger in initiating ice ages is the changing positions of Earth’s ever-moving continents, which affect ocean and atmospheric circulation patterns. When plate-tectonic movement causes continents to be arranged such that warm water flow from the equator to the poles is blocked or reduced, ice sheets may arise and set another ice age in motion. Today’s ice age most likely began when the land bridge between North and South America (Isthmus of Panama) formed and ended the exchange of tropical water between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, significantly altering ocean currents.
Glacials and interglacials occur in fairly regular repeated cycles. The timing is governed to a large degree by predictable cyclic changes in Earth’s orbit, which affect the amount of sunlight reaching different parts of Earth’s surface. The three orbital variations are: (1) changes in Earth’s orbit around the Sun (eccentricity), (2) shifts in the tilt of Earth’s axis (obliquity), and (3) the wobbling motion of Earth’s axis (precession).
How do we know about past ice ages?
Scientists have reconstructed past ice ages by piecing together information derived from studying ice cores, deep sea sediments, fossils, and landforms.
Ice and sediment cores reveal an impressive detailed history of global climate. Cores are collected by driving long hollow tubes as much as 2 miles deep into glacial ice or ocean floor sediments. Ice cores provide annual and even seasonal climate records for up to hundreds of thousands of years, complementing the millions of years of climate records in ocean sediment cores.
Within just the past couple of decades, ice cores recovered from Earth’s two existing ice sheets, Greenland and Antarctica, have revealed the most detailed climate records yet.
Do ice ages come and go slowly or rapidly?
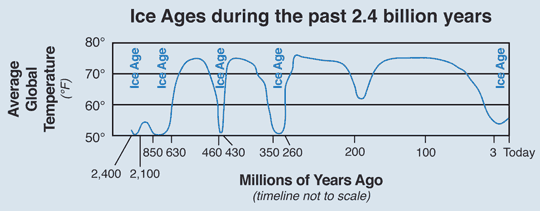
Simplified chart showing when the five major ice ages occurred in the past 2.4 billion years of Earth’s history. Modified from several sources including Dynamical Paleoclimatology: Generalized Theory of Global Climate Change, 2002, by Barry Saltzman.
Records show that ice ages typically develop slowly, whereas they end more abruptly. Glacials and interglacials within an ice age display this same trend.
On a shorter time scale, global temperatures fluctuate often and rapidly. Various records reveal numerous large, widespread, abrupt climate changes over the past 100,000 years. One of the more recent intriguing findings is the remarkable speed of these changes. Within the incredibly short time span (by geologic standards) of only a few decades or even a few years, global temperatures have fluctuated by as much as 15°F (8°C) or more. For example, as Earth was emerging out of the last glacial cycle, the warming trend was interrupted 12,800 years ago when temperatures dropped dramatically in only several decades. A mere 1,300 years later, temperatures locally spiked as much as 20°F (11°C) within just several years. Sudden changes like this occurred at least 24 times during the past 100,000 years. In a relative sense, we are in a time of unusually stable temperatures today—how long will it last?
The warming we have experienced since the Industrial Revolution is not part of any glacial/interglacial cycle. The Earth had been cooling for over 5,000 years and was on its way to another glacial period within 10-25,000 years when manmade global warming began. The rate at which the Earth is warming, right now, is 5-10
times faster than it has ever warmed in the last
million years. Atmospheric CO2 levels, right now, are higher than they have been at
any point on this planet in the last
3 million years. Please take a half a minute and think about those two facts. The problem with global warming has NEVER BEEN the absolute temperature. It is the rate at which CO2 is climbing and the rate at which that is making us warm.