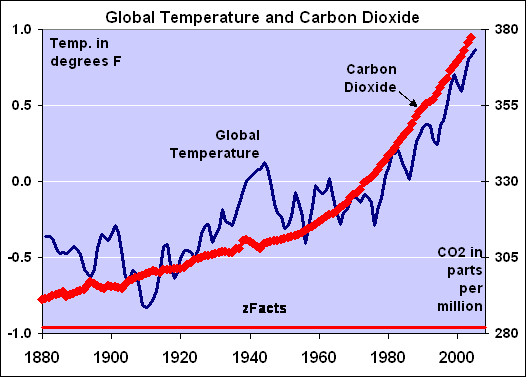
Let me see.. The IPCC originally said that CO2 will cause 4-6 deg C. warming per doubling... Then the earth didn't comply with their directive and less than 0.03 hundredths of a degree could even remotely be attributed to CO2 'back radiation'. So they lowered their estimates to 1 deg C per doubling and the pause happened throwing this prediction into the garbage.. now they are toying with 0.3 to 0.6 deg C per doubling .. Yet the empirical evidence says that we are at a zero influence attribution to CO2 today...
SO either your photons are having little to no effect or the water cycle on earth is laying the runaway theory falsified... To date no one has done the science to determine which it is.. Historical evidence suggests that CO2 and its 'back radiation' have had no effect in the past. So i side with the laws of thermal dynamics which state that a cooler object can not effect a warmer one.
Are photons being emitted? Yes... Can they strike cooler objects? Yes.. It is the effect on the cooler matter that no one has proven through empirical, observed evidence.. You would have some magical photons that can defy thermal dynamics and heat transfer laws to have an impact.
Let me see.. The IPCC originally said that CO2 will cause 4-6 deg C. warming per doubling...
I already told you I'm not interested in liberal lies about AGW, I just want to discuss the physics.
SO either your photons are having little to no effect
Great, lets talk about photons.
i side with the laws of thermal dynamics which state that a cooler object can not effect a warmer one.
Since we aren't talking about objects in contact with each other, but photons traveling freely in all directions, your confused understanding of thermodynamics and "smart photons" doesn't apply.
Please tell me what you think those photons are doing.
As I understand the laws of EM wave propagation, it tells me that those photons, emitted from a warmer object, are at shorter wavelength. And those emitted from a cooler object are at a longer wavelength. Thus the energy they carry is less than the energy carried by the warmer. The loss of the warmer object dwarfs any warming which might be caused by the cooler by factors of 10^6 order.
To get a better picture of why BBR can not warm the hotter object one needs to simply look at the power differential of the waves being propagated. The laws of thermal dynamics and why a cooler objects can not warm a hotter objects, in very simple terms.
Please tell me what you think those photons are doing.
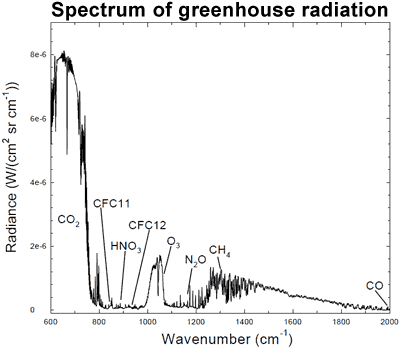
Photons from CO2 and H2O in the atmosphere? They travel in random directions, sometimes toward space, sometimes toward the ground.
photons, emitted from a warmer object, are at shorter wavelength. And those emitted from a cooler object are at a longer wavelength.
Yes.
Thus the energy they carry is less than the energy carried by the warmer.
Yes again.
The loss of the warmer object dwarfs any warming which might be caused by the cooler
Yes yet a third time. I'll ignore the bad math at the end of that last sentence.
To get a better picture of why BBR can not warm the hotter object
Here is where you go off the tracks.
The laws of thermal dynamics and why a cooler objects can not warm a hotter objects,
Again, we're talking about photons, not objects in contact.
I don't think anyone here has ever claimed that radiation from the 70 degree ground is emitted into the atmosphere, absorbed by GHGs and re-emitted to the ground, causing the ground to warm to 71 degrees.
Here is what back radiation does, it simply slows the rate of cooling. The warmer object, in this case the ground, still cools. Still emits more photons to the atmosphere than it receives back from the atmosphere.
There is no violation of the laws of thermodynamics (not thermal dynamics FFS).
There is no need for the emitter, or the photon, to measure the temperature of the surroundings before deciding where, or if, to emit a photon.
The Stefan Boltzmann constant shows that energy emitted is based on the 4th power of the temperature.
So if the ground is 293K and the atmosphere is 273K, ignoring for the moment the different emissivity of each, the ground will emit about 33% more energy than the atmosphere. The ground still cools, back radiation just slows the cooling, because some energy is coming back down.
In the desert, less H20 means faster cooling because there is less energy coming back down and more escaping more quickly into space. When the Sun sets on the Moon, the lack of any back radiation, because of the lack of any atmosphere, is further evidence of the point we're trying to show you.