West Antarctic is the second largest "national" region on Earth, falling between Russia and Canada, but this is still regional and even within West Antarctica, the trend is not uniform.
West Antarctica is largely covered by the
Antarctic ice sheet, but there have been signs that
climate change is having some effect and that this ice sheet may have started to shrink slightly.
Over the past 50 years, the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula has been – and still is – one of the most rapidly warming parts of the planet,
[1][2] and the coasts of the Peninsula are the only parts of West Antarctica that become (in summer) ice-free. These constitute the
Marielandia Antarctic tundra and have the warmest climate in Antarctica. The rocks are clad in
mosses and
lichens that can cope with the intense cold of winter and the short growing-season.
- "Impacts of climate change". Discovering Antarctica. Retrieved 2021-11-20.
- ^ "WMO verifies one temperature record for Antarctic continent and rejects another". public.wmo.int. 2021-06-30. Retrieved 2021-11-20.

en.wikipedia.org
The world as a whole has - as you all already know - done this:
View attachment 857427

data.giss.nasa.gov
View attachment 857429
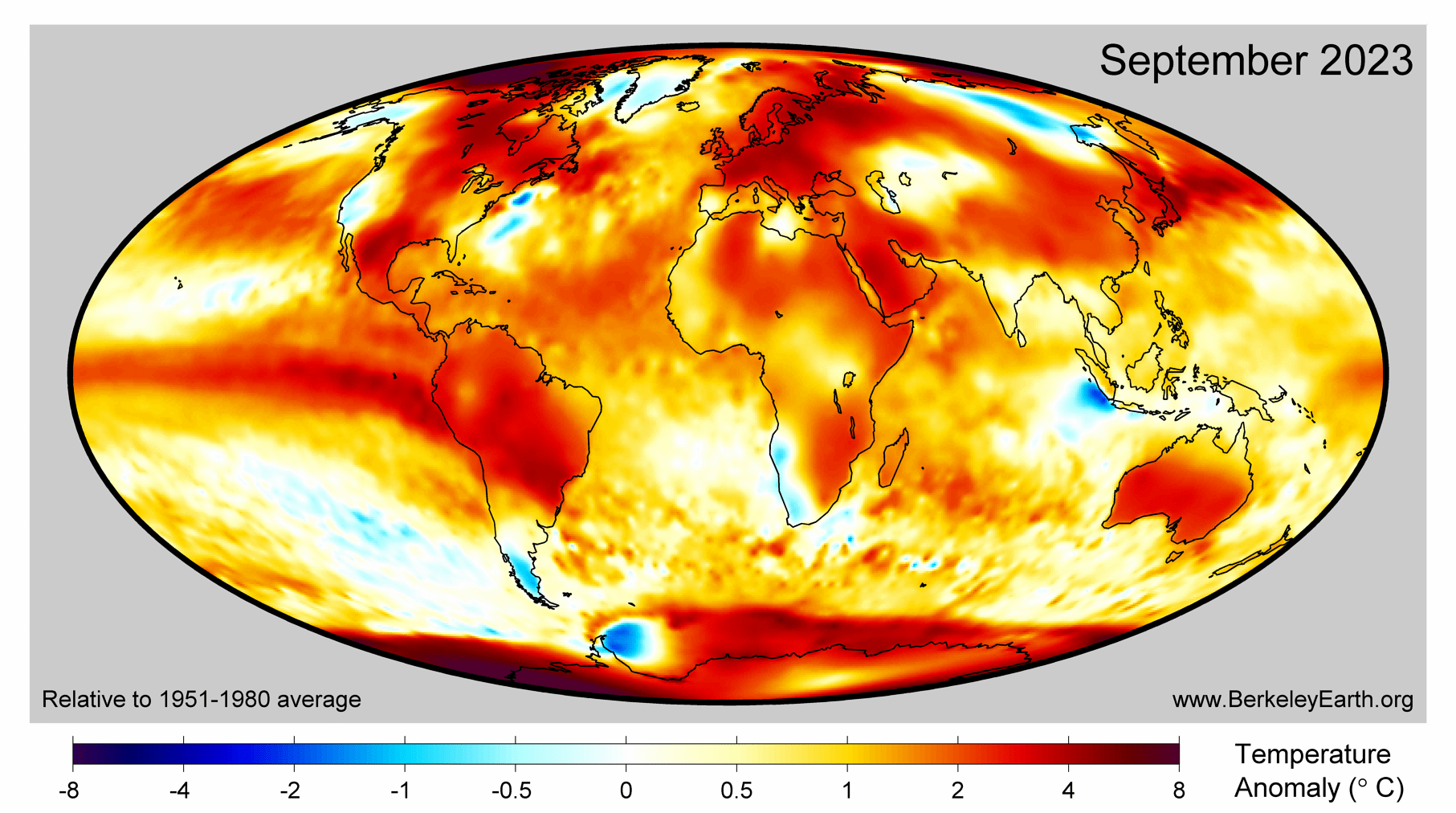
September 2023 was the warmest since records began in 1850. 2023 is virtually certain to become a record warm year, and likely to exceed 1.5 °C.

berkeleyearth.org
View attachment 857431
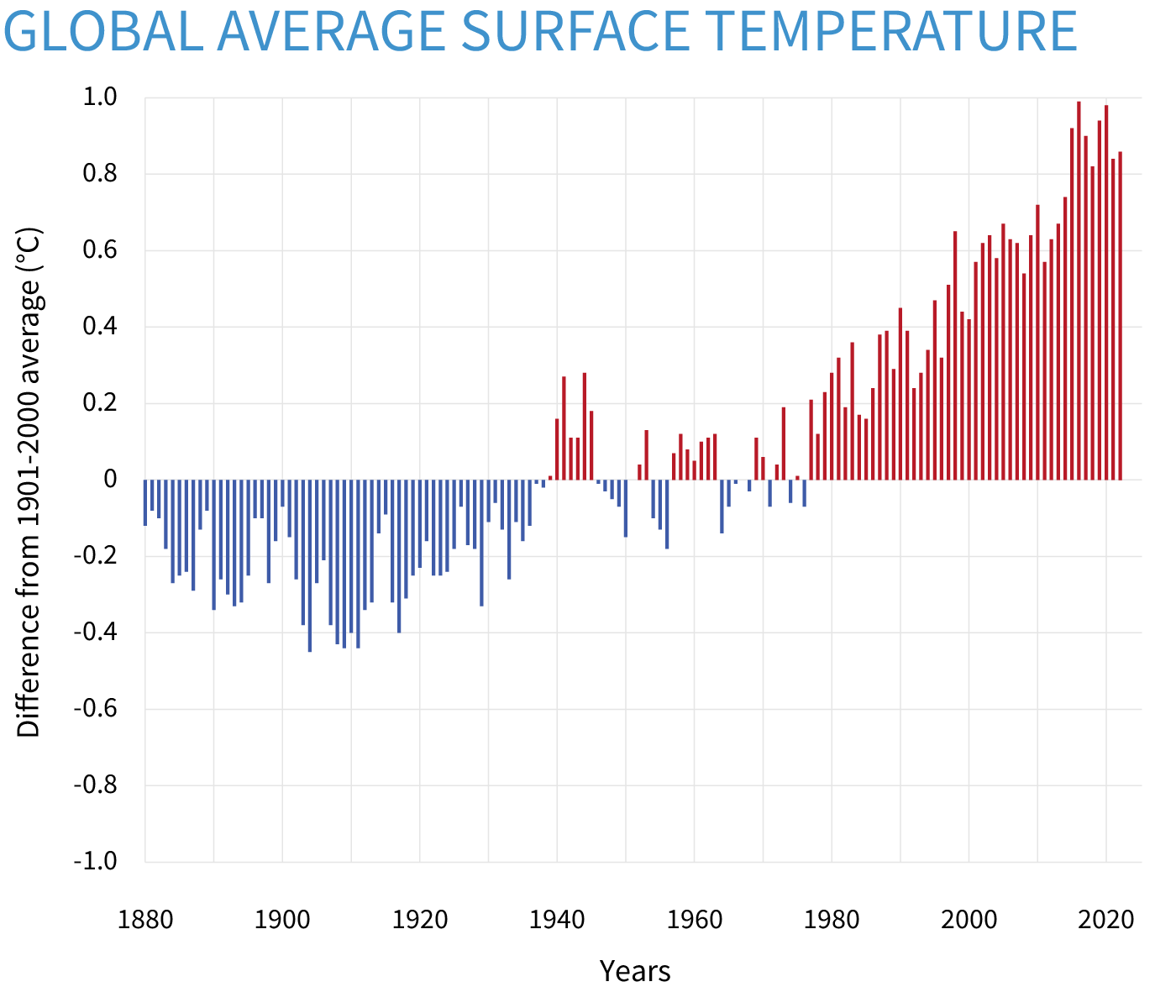
Earth's surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the start of the NOAA record in 1850. It may seem like a small change, but it's a tremendous increase in stored heat.

www.climate.gov