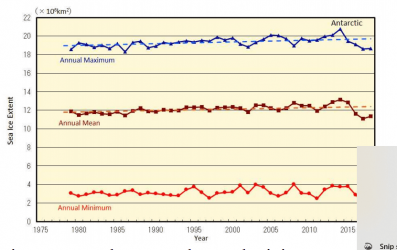
Ice loss in the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) dwarfs minute gains in East Antarctica and Greenland has lost almost twice as much. Here, of course, is where our deniers start yammering about volcanoes under the ice.
 science.sciencemag.org
science.sciencemag.org
and

 earthsky.org
earthsky.org
Science | AAAS
and

| EarthSky
Using satellite data, scientists have made precise, detailed maps of how the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets have changed over 16 years. How the maps were made, and what they tell us.