As Arctic Ocean warms, megatonnes of methane bubble up - environment - 17 August 2009 - New Scientist
It's been predicted for years, and now it's happening. Deep in the Arctic Ocean, water warmed by climate change is forcing the release of methane from beneath the sea floor.
Over 250 plumes of gas have been discovered bubbling up from the sea floor to the west of the Svalbard archipelago, which lies north of Norway. The bubbles are mostly methane, which is a greenhouse gas much more powerful than carbon dioxide.
The methane is probably coming from reserves of methane hydrate beneath the sea bed. These hydrates, also known as clathrates, are water ice with methane molecules embedded in them.
The methane plumes were discovered by an expedition aboard the research ship James Clark Ross, led by Graham Westbrook of the University of Birmingham and Tim Minshull of the National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, both in the UK
Hi oldie,
I have a few problems with this story you posted. First of all it assumes the plumes are coming from methane hydrates and while they admit that the methane could be from a primary source they think it unlikely because of the amount of gas...I guess they are unfamiliar with the spill currently going on in the Gulf.
The problem with the hydrate theory is the simple fact that methane hydrate really does exist in a very narrow range. And not where they are finding the plumes.
https://www.llnl.gov/str/Durham.html
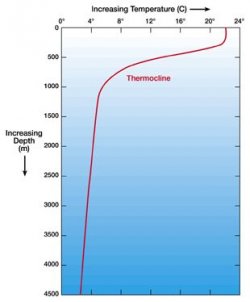
Has a very nice comprehensive view of methane hydrate formation and stability issues. Please note that at the low depths associated with the archipelago there is neither the pressure nor the low temperature to form the hydrates in the first place. At high preassure the hydrates can survive up to a temperature of 275 kelvin which is 2 degrees above freezing. At low pressures such as at low depth that drops to around 225 kelvin which is the temp you find in a lab and nowhere else.
The graph below shows the temperature drop with depth and as you can see the depth of the archipelago is above the thermocline.
If you have any further information on this I would love to see it.
Attachments
Last edited: