That brings an interesting quiz to mind.Yanking your own chain like that is called mental masturbation....you let me know when you get an observed, measured instance of back radiation gathered with an instrument at ambient temperature.
As we've pointed out before, anyone can buy a longwave IR camera, one that works at ambient temperature, which does exactly that. Point it at the sky, it displays in image showing the differing temperatures of clouds and sky. It is clearly measuring the IR radiation coming down from the very cold sky. That is, the backradiation.
We've also pointed out that sensors never needed to be chilled to measure backradiation. Chilling just lowered the thermal noise, making the image clearer. Modern electronics found around around that need for chilling.
Now, wait until you see how SSDD handwaves that away. It's both hilarious and pathetic.
Suppose you point an IR sensor at a target which is an ice cube right next to another same sized object which is at +20C. How many watts/m^2 should you see on the instrument`s display?
The ice cube @ 0 C radiates just under 314 w/m^2 and the 20 degC object radiates almost 418 w/m^
I take it you would say that the instrument would display the sum of both, a total of 732 w/m^2 ?
And if I can get only 400 watts/m^2 you would say that there is something wrong with my IR gun?
Buy one and try it out. Maybe you can come up with an explanation why it`s never higher than that. Off the shelf these are calibrated for Temperature but from that you can calculate the watts/m^ 2. Mine has a laser pointer so it`s quite easy to center it and you can find out the proper distance just as easily if you move back till the indicated temperature deviates to below the known temperature of the target.
I also have a thermal imaging camera, but it does not have a USB to connect to another storage device else I would upload some pictures.
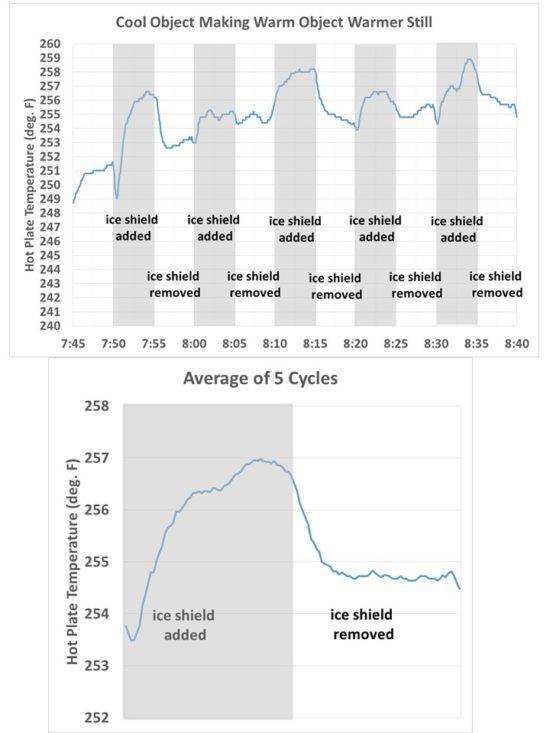
If I put a cold object next to a warm one, the side of the warm object facing the cold one shows up cooler than the rest of that object...conforming to "a cold object can make a warm object even warmer" my camera should not see what it is seeing...explain that
Been drinking Bernie?
Accusing crick of believing that a gallon of 10C water added to a gallon of 40C water will result in 50C water is pretty low even for you.
If it is minus 20C outside your warm object will be warmer if you put a block of ice at only minus 5C next to it. So what was your point?