- Thread starter
- #201
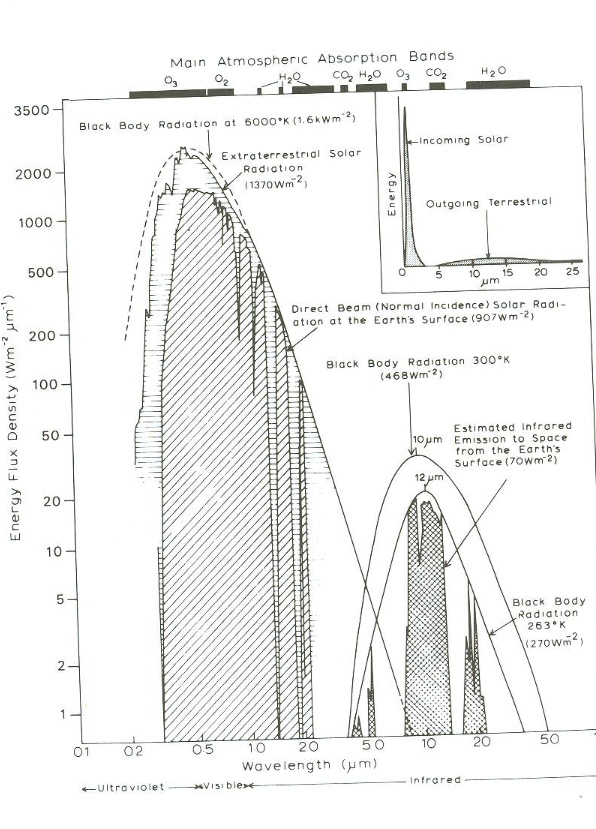
Climate science says that the earth radiates at a certain wattage per square meter and at a certain wavelength....that implies a certain temperature...or didn't you know that?At what temperature does the earth radiate and at what wavelength?
It's further evidence your silliness that you imply that the earth would necessarily radiate at a single temperature and wavelength.
If you actually did any thinking, you would have understood the fundamental error you're making here. Here - among other data, are the range of wavelengths (PLURAL, ~5-50 microns) at which the Earth radiates.
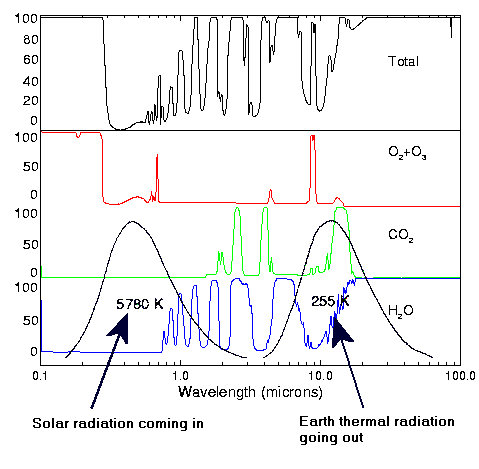
You are SO stupid!
Last edited: