Stratospheric Cooling and Tropospheric Warming
Posted on 1 December 2010 by Bob Guercio
This post has been revised at Stratospheric Cooling and Tropospheric Warming - Revised
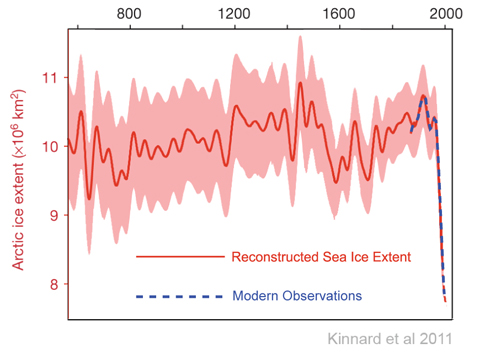
Increased levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere have resulted in the warming of the troposphere and cooling of the stratosphere. This paper will explain the mechanism involved by considering a model of a fictitious planet with an atmosphere consisting of carbon dioxide and an inert gas such as nitrogen at pressures equivalent to those on earth. This atmosphere will have a troposphere and a stratosphere with the tropopause at 10 km. The initial concentration of carbon dioxide will be 100 parts per million (ppm) and will be increased instantaneously to 1000 ppm and the solar insolation will be 385.906 watts/meter2. Figure 1 is the IR spectrum from a planet with no atmosphere and Figures 2 and 3 represent the same planet with levels of CO2 at 100 ppm and 1000 ppm respectively. These graphs were generated from a model simulator at the website of Dr. David Archer, a professor in the Department of the Geophysical Sciences at the University of Chicago and edited to contain only the curves of interest to this discussion. The parameters were chosen in order to generate diagrams that enable the reader to more easily understand the mechanism discussed herein.
I don't WANT a fictious planet with no other constituent gases or particles than CO2 and Nitrogen. I want to know how the Combined absorption of WATER VAPOR and CO2 does not saturate in the LOWER atmos and CO2 increases in the UPPER atmos (where there IS no water vapor) don't matter.
One of blog comments pretty well sums up the frustration I'm describing..
For one thing, I'm not sure that there even would be a stratosphere (ie with temperatures increasing with height) if there was no oxygen/ozone in the atmosphere as there is in your model. So it may not make sense to talk about a warmer lower atmosphere causing an even cooler upper atmosphere in such a simplified case.
Also, I understand that other variations, in water vapour, volcanic aerosols, chlorofluorocarbons and methane concentrations, can cause temperature changes in the stratosphere.
Having said that, I don't actually doubt that rising CO2 does result in a cooling stratosphere, I'm just struggling to understand how exactly and by how much.
Crap, Flatulance, try reading some scientific material from peer reviewed journals, instead of blogs. One should seek knowledge from those more intelligent or knowledgable than themselves, not misinformation from those equally ignorant.
You MF'ing MORON!!! You just wasted my time sending me to a FUCKING BLOG SITE where the AUTHOR of the explanation admits in the Discussion section...
I'm saying a lot here but I must stress that I am very much an amateur at this and may not be totally correct.I'm also a bit tired and may not be writing very clearly.
Bob
And YOU have the BALLS to tell me read PEER REVIEWED LITERATURE!!
Hopeless Hypocrit.. And Pathetic... I need a SERIOUS answer....