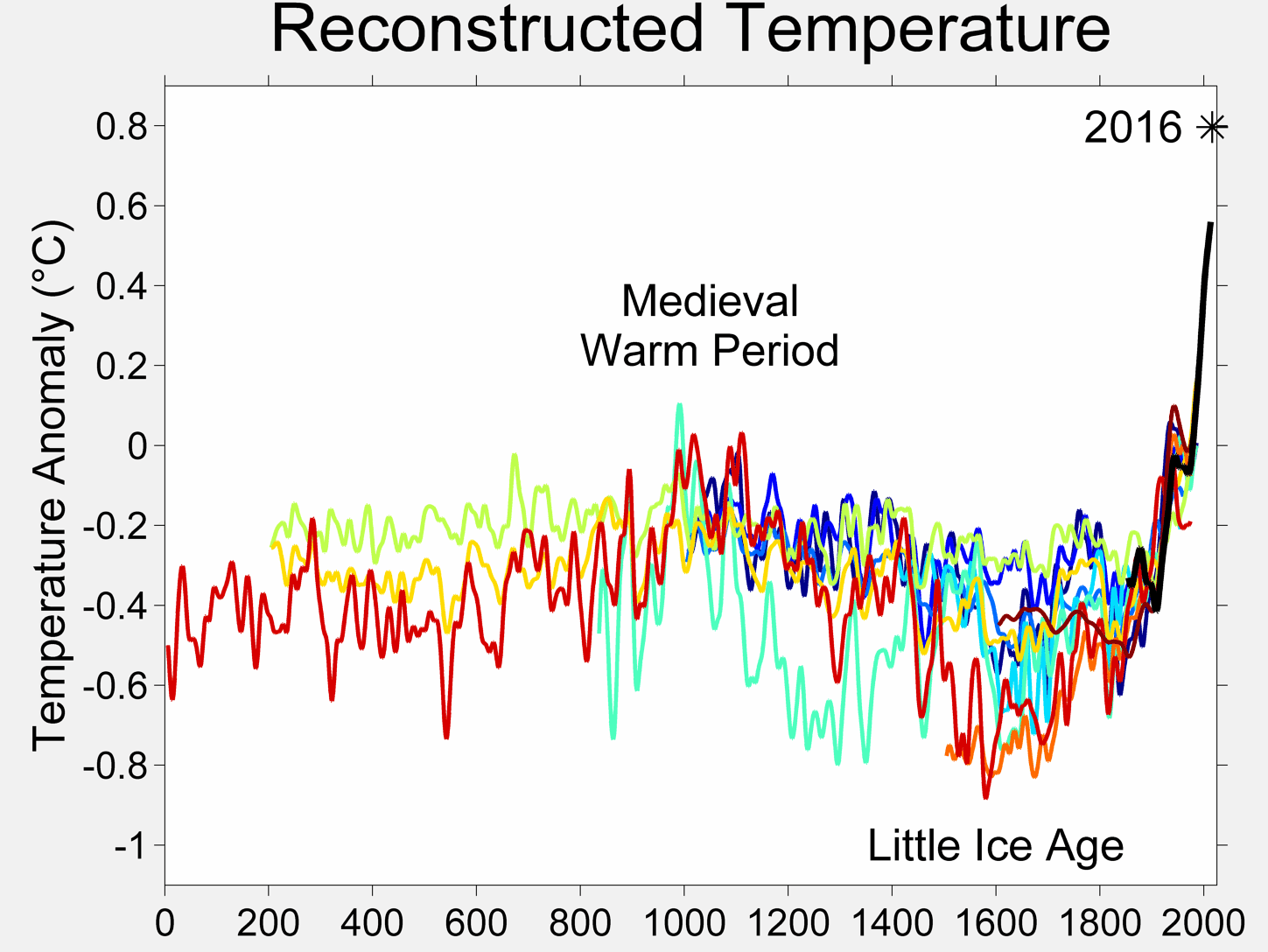
Old Rocks
Diamond Member
From tobacco to asbestos, to global warming we see the same cast of people denying real science.
Wunder Blog : Weather Underground
Posted by: JeffMasters, 3:07 PM GMT on November 25, 2009
In 1954, the tobacco industry realized it had a serious problem. Thirteen scientific studies had been published over the preceding five years linking smoking to lung cancer. With the public growing increasingly alarmed about the health effects of smoking, the tobacco industry had to move quickly to protect profits and stem the tide of increasingly worrisome scientific news. Big Tobacco turned to one the world's five largest public relations firms, Hill and Knowlton, to help out. Hill and Knowlton designed a brilliant Public Relations (PR) campaign to convince the public that smoking is not dangerous. They encouraged the tobacco industry to set up their own research organization, the Council for Tobacco Research (CTR), which would produce science favorable to the industry, emphasize doubt in all the science linking smoking to lung cancer, and question all independent research unfavorable to the tobacco industry. The CTR did a masterful job at this for decades, significantly delaying and reducing regulation of tobacco products. George Washington University epidemiologist David Michaels, who is President Obama's nominee to head the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA), wrote a meticulously researched 2008 book called, Doubt is Their Product: How Industry's Assault on Science Threatens Your Health. In the book, he wrote: "the industry understood that the public is in no position to distinguish good science from bad. Create doubt, uncertainty, and confusion. Throw mud at the anti-smoking research under the assumption that some of it is bound to stick. And buy time, lots of it, in the bargain". The title of Michaels' book comes from a 1969 memo from a tobacco company executive: "Doubt is our product since it is the best means of competing with the 'body of fact' that exists in the minds of the general public. It is also the means of establishing a controversy". Hill and Knowlton, on behalf of the tobacco industry, had founded the "Manufactured Doubt" industry.
The Manufactured Doubt industry grows up
As the success of Hill and Knowlton's brilliant Manufactured Doubt campaign became apparent, other industries manufacturing dangerous products hired the firm to design similar PR campaigns. In 1967, Hill and Knowlton helped asbestos industry giant Johns-Manville set up the Asbestos Information Association (AIA). The official-sounding AIA produced "sound science" that questioned the link between asbestos and lung diseases (asbestos currently kills 90,000 people per year, according to the World Health Organization). Manufacturers of lead, vinyl chloride, beryllium, and dioxin products also hired Hill and Knowlton to devise product defense strategies to combat the numerous scientific studies showing that their products were harmful to human health.
By the 1980s, the Manufactured Doubt industry gradually began to be dominated by more specialized "product defense" firms and free enterprise "think tanks". Michaels wrote in Doubt is Their Product about the specialized "product defense" firms: "Having cut their teeth manufacturing uncertainty for Big Tobacco, scientists at ChemRisk, the Weinberg Group, Exponent, Inc., and other consulting firms now battle the regulatory agencies on behalf of the manufacturers of benzene, beryllium, chromium, MTBE, perchlorates, phthalates, and virtually every other toxic chemical in the news today....Public health interests are beside the point. This is science for hire, period, and it is extremely lucrative".
Joining the specialized "product defense" firms were the so-called "think tanks". These front groups received funding from manufacturers of dangerous products and produced "sound science" in support of their funders' products, in the name of free enterprise and free markets. Think tanks such as the George C. Marshall Foundation, Competitive Enterprise Institute, Heartland Institute, and Dr. Fred Singer's SEPP (Science and Environmental Policy Project) have all been active for decades in the Manufactured Doubt business, generating misleading science and false controversy to protect the profits of their clients who manufacture dangerous products.
Wunder Blog : Weather Underground
Posted by: JeffMasters, 3:07 PM GMT on November 25, 2009
In 1954, the tobacco industry realized it had a serious problem. Thirteen scientific studies had been published over the preceding five years linking smoking to lung cancer. With the public growing increasingly alarmed about the health effects of smoking, the tobacco industry had to move quickly to protect profits and stem the tide of increasingly worrisome scientific news. Big Tobacco turned to one the world's five largest public relations firms, Hill and Knowlton, to help out. Hill and Knowlton designed a brilliant Public Relations (PR) campaign to convince the public that smoking is not dangerous. They encouraged the tobacco industry to set up their own research organization, the Council for Tobacco Research (CTR), which would produce science favorable to the industry, emphasize doubt in all the science linking smoking to lung cancer, and question all independent research unfavorable to the tobacco industry. The CTR did a masterful job at this for decades, significantly delaying and reducing regulation of tobacco products. George Washington University epidemiologist David Michaels, who is President Obama's nominee to head the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA), wrote a meticulously researched 2008 book called, Doubt is Their Product: How Industry's Assault on Science Threatens Your Health. In the book, he wrote: "the industry understood that the public is in no position to distinguish good science from bad. Create doubt, uncertainty, and confusion. Throw mud at the anti-smoking research under the assumption that some of it is bound to stick. And buy time, lots of it, in the bargain". The title of Michaels' book comes from a 1969 memo from a tobacco company executive: "Doubt is our product since it is the best means of competing with the 'body of fact' that exists in the minds of the general public. It is also the means of establishing a controversy". Hill and Knowlton, on behalf of the tobacco industry, had founded the "Manufactured Doubt" industry.
The Manufactured Doubt industry grows up
As the success of Hill and Knowlton's brilliant Manufactured Doubt campaign became apparent, other industries manufacturing dangerous products hired the firm to design similar PR campaigns. In 1967, Hill and Knowlton helped asbestos industry giant Johns-Manville set up the Asbestos Information Association (AIA). The official-sounding AIA produced "sound science" that questioned the link between asbestos and lung diseases (asbestos currently kills 90,000 people per year, according to the World Health Organization). Manufacturers of lead, vinyl chloride, beryllium, and dioxin products also hired Hill and Knowlton to devise product defense strategies to combat the numerous scientific studies showing that their products were harmful to human health.
By the 1980s, the Manufactured Doubt industry gradually began to be dominated by more specialized "product defense" firms and free enterprise "think tanks". Michaels wrote in Doubt is Their Product about the specialized "product defense" firms: "Having cut their teeth manufacturing uncertainty for Big Tobacco, scientists at ChemRisk, the Weinberg Group, Exponent, Inc., and other consulting firms now battle the regulatory agencies on behalf of the manufacturers of benzene, beryllium, chromium, MTBE, perchlorates, phthalates, and virtually every other toxic chemical in the news today....Public health interests are beside the point. This is science for hire, period, and it is extremely lucrative".
Joining the specialized "product defense" firms were the so-called "think tanks". These front groups received funding from manufacturers of dangerous products and produced "sound science" in support of their funders' products, in the name of free enterprise and free markets. Think tanks such as the George C. Marshall Foundation, Competitive Enterprise Institute, Heartland Institute, and Dr. Fred Singer's SEPP (Science and Environmental Policy Project) have all been active for decades in the Manufactured Doubt business, generating misleading science and false controversy to protect the profits of their clients who manufacture dangerous products.