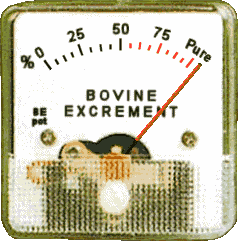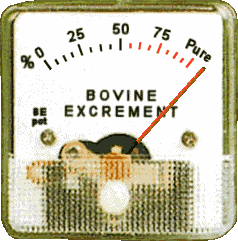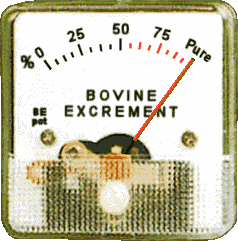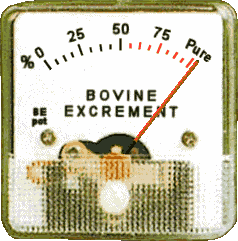
There will be blood, and hell to pay for this. These idiots do not realize the Pandora's box they just opened on themselves. For the gun owners of New York: Do not give in to their demands. You have your rights.
The Second Amendment:
A well regulated militia, being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear arms, shall not be infringed.
You forgot to cite the case where a court ruled the law was un-Constitutional.
And the Second Amendment, as with the rest of the Constitution, exists only in the context of its case law; to simply cite an Amendment absent that context is ignorant and meaningless – as is the rest of your ridiculous, hyperbolic post.
District of Columbia vs Heller
DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA v. HELLER
Justice Scalia, Opinion of the Court
NOTICE: This opinion is subject to formal revision before publication in the preliminary print of the United States Reports. Readers are requested to notify the Reporter of Decisions, Supreme Court of the United States, Washington, D. C. 20543, of any typographical or other formal errors, in order that corrections may be made before the preliminary print goes to press.
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA, et al., PETITIONERS v.
DICK ANTHONY HELLER
on writ of certiorari to the united states court ofappeals for the district of columbia circuit
[June 26, 2008]
Justice Scalia delivered the opinion of the Court.
We consider whether a District of Columbia prohibition on the possession of usable handguns in the home violates the Second Amendment to the Constitution.
Respondent Dick Heller is a D. C. special police officer authorized to carry a handgun while on duty at the Federal Judicial Center. He applied for a registration certificate for a handgun that he wished to keep at home, but the District refused. He thereafter filed a lawsuit in the Federal District Court for the District of Columbia seeking, on Second Amendment grounds, to enjoin the city from enforcing the bar on the registration of handguns, the licensing requirement insofar as it prohibits the carrying of a firearm in the home without a license, and the trigger-lock requirement insofar as it prohibits the use of “functional firearms within the home.” App. 59a. The District Court dismissed respondent’s complaint, see Parker v. District of Columbia, 311 F. Supp. 2d 103, 109 (2004). The Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit, construing his complaint as seeking the right to render a firearm operable and carry it about his home in that condition only when necessary for self-defense,2 reversed, see Parker v. District of Columbia, 478 F. 3d 370, 401 (2007). It held that the Second Amendment protects an individual right to possess firearms and that the city’s total ban on handguns, as well as its requirement that firearms in the home be kept nonfunctional even when necessary for self-defense, violated that right. See id., at 395, 399–401. The Court of Appeals directed the District Court to enter summary judgment for respondent.
We granted certiorari. 552 U. S. ___ (2007).
From our review of founding-era sources, we conclude that this natural meaning was also the meaning that “bear arms” had in the 18th century. In numerous instances, “bear arms” was unambiguously used to refer to the carrying of weapons outside of an organized militia. The most prominent examples are those most relevant to the Second Amendment : Nine state constitutional provisions written in the 18th century or the first two decades of the 19th, which enshrined a right of citizens to “bear arms in defense of themselves and the state” or “bear arms in defense of himself and the state.” 8 It is clear from those formulations that “bear arms” did not refer only to carrying a weapon in an organized military unit. Justice James Wilson interpreted the Pennsylvania Constitution’s arms-bearing right, for example, as a recognition of the natural right of defense “of one’s person or house”—what he called the law of “self preservation.” 2 Collected Works of James Wilson 1142, and n. x (K. Hall & M. Hall eds. 2007) (citing Pa. Const., Art. IX, §21 (1790)); see also T. Walker, Introduction to American Law 198 (1837) (“Thus the right of self-defence [is] guaranteed by the [Ohio] constitution”

; see also id., at 157 (equating Second Amendment with that provision of the Ohio Constitution). That was also the interpretation of those state constitutional provisions adopted by pre-Civil War state courts.9 These provisions demonstrate—again, in the most analogous linguistic context—that “bear arms” was not limited to the carrying of arms in a militia.