Toddsterpatriot
Diamond Member
Its called rate of release in comparison with its surroundings. The greater the differential the faster the release..Can a colder object cause a warmer object to cool more slowly?
Typical that you would ask, rather than answer the question for yourself. Refer to the SB equation for an object radiating into something other than a vacuum. Here....let me help you.
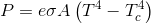
Lets make the radiator 1 square meter with an emissivity of 1 for simplicity's sake and lets make the temperature of the radiator 75F
If it is radiating into a background that is 73F then P = 65.1 watts
If it is radiating into a background that is 45F then P = 92.06 watts
If it is radiating into a background that is 25F then P = 107.46 watts
So clearly, as the background temperature drops, the amount of energy the radiator emits increases, and conversely, as the background temperature increases, the amount of energy that the radiator emits decreases till such time as the temperature of the background and the emitter are the same and the amount of energy the radiator is emitting is zero.
If it is radiating into a background that is 73F then P = 65.1 watts
If it is radiating into a background that is 45F then P = 92.06 watts
If it is radiating into a background that is 25F then P = 107.46 watts
Dimmer switch!!!
Its called rate of release in comparison with its surroundings.
Yup, it's a dimmer switch.
So how does the emitter know the temperature of the surroundings?
You know, so it can adjust the rate.......