I am still waiting for the AGW cult to prove with datasets and source code that proves their religion.
Have yet to see it materialize.
Have yet to see it materialize.
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.

Note: This feature currently requires accessing the site using the built-in Safari browser.
I am still waiting for the AGW cult to prove with datasets and source code that proves their religion.
Have yet to see it materialize.
Do you lose heat faster in a freezer? If so, let's hear your explanation why.
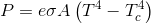 which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.
which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.Do you lose heat faster in a freezer? If so, let's hear your explanation why.
So you believe in cold rays? Cold emanations? Pictet did some experiments way back when in the ladder part of the 18th century, and thought that he had discovered cold emanations...that cold objects radiated to warm.
If cold can be radiated to warm, I can think of some damned fine and profitable uses. Name one. There are literally thousands of heat radiation applications on the market...name one cold radiation application.
You crack me up...cold emanations...cold rays...hey guys, lets build a freeze ray!!!! haahahhahahhah
If you want to know why you lose heat faster in a freezer than you do in the cold refer to the Stefan Boltzman Law...which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.
He doesn't have one. That he compares the flow of photons to the flow of water just illustrates the naivete of his thinking. Photons do not interact with each other, only with matter.
Do you lose heat faster in a freezer? If so, let's hear your explanation why.
So you believe in cold rays? Cold emanations? Pictet did some experiments way back when in the ladder part of the 18th century, and thought that he had discovered cold emanations...that cold objects radiated to warm.
If cold can be radiated to warm, I can think of some damned fine and profitable uses. Name one. There are literally thousands of heat radiation applications on the market...name one cold radiation application.
You crack me up...cold emanations...cold rays...hey guys, lets build a freeze ray!!!! haahahhahahhah
If you want to know why you lose heat faster in a freezer than you do in the cold refer to the Stefan Boltzman Law...which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.
How does the radiator know the temperature of its surroundings? Does it read a thermometer? LOL!
You still haven't given me the mechanism that shuts off emissions, when a warmer object approaches.
Or the one that explains faster emission in a cooler environment.
Let's hear it.
mechanism manages to explain both. Let's hear yours, already.
He doesn't have one. That he compares the flow of photons to the flow of water just illustrates the naivete of his thinking. Photons do not interact with each other, only with matter.
Do you lose heat faster in a freezer? If so, let's hear your explanation why.
So you believe in cold rays? Cold emanations? Pictet did some experiments way back when in the ladder part of the 18th century, and thought that he had discovered cold emanations...that cold objects radiated to warm.
If cold can be radiated to warm, I can think of some damned fine and profitable uses. Name one. There are literally thousands of heat radiation applications on the market...name one cold radiation application.
You crack me up...cold emanations...cold rays...hey guys, lets build a freeze ray!!!! haahahhahahhah
If you want to know why you lose heat faster in a freezer than you do in the cold refer to the Stefan Boltzman Law...which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant, symbolized by the lowercase Greek letter sigma ( ), is a physical constant involving black body radiation. A black body, also called an ideal radiator, is an object that radiates or absorbs energy with perfect efficiency at all electromagnetic wavelength s. The constant defines the power per unit area emitted by a black body as a function of its thermodynamic temperature .
How does the radiator know the temperature of its surroundings? Does it read a thermometer? LOL!
You really are beginning to sound like a very boring idiot. How does the air inside a punctured tire know that the pressure is lower outside and thus, it is time to escape? Why do you think a thing, subject to the forces of nature must "know" what to do?
You still haven't given me the mechanism that shuts off emissions, when a warmer object approaches.
I will give you that mechanism as soon as you give me the mechanism which causes gravity. Gravity should be an easy one, so lets here what makes gravity work.
Or the one that explains faster emission in a cooler environment.
Let's hear it.
Already gave it to you...or do you not think the SB law applies?
mechanism manages to explain both. Let's hear yours, already.
Your mechanism is an artifact of a mathematical model...nothing more. Unobservable, unmeasurable, untestable....a product of your faith.
So you believe in cold rays? Cold emanations? Pictet did some experiments way back when in the ladder part of the 18th century, and thought that he had discovered cold emanations...that cold objects radiated to warm.
If cold can be radiated to warm, I can think of some damned fine and profitable uses. Name one. There are literally thousands of heat radiation applications on the market...name one cold radiation application.
You crack me up...cold emanations...cold rays...hey guys, lets build a freeze ray!!!! haahahhahahhah
If you want to know why you lose heat faster in a freezer than you do in the cold refer to the Stefan Boltzman Law...which describes the amount of energy a radiator loses depending upon the temperature difference between the radiator and its cooler surroundings. Note: the equation describes a one way gross energy flow from warm to cool...not a two way net flow.
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant, symbolized by the lowercase Greek letter sigma ( ), is a physical constant involving black body radiation. A black body, also called an ideal radiator, is an object that radiates or absorbs energy with perfect efficiency at all electromagnetic wavelength s. The constant defines the power per unit area emitted by a black body as a function of its thermodynamic temperature .
So are you saying that the SB law only applies to perfect blackbodies? If that is true, you just trashed the greenhouse hypothesis and everything that came out of it. All garbage...back to the drawing board. Maybe next time they will come up with a hypothesis that can predict the temperatures of other planets, as well as earth.
He has confused (and I'm being generous with that term) net heat transfer with absolute heat transfer. Rather than the scenario in which all items radiate per their temperature, in SSDD's universe, only hotter things radiate to colder, and - somehow - the amount of that radiation is throttled depending on the delta T. All that is necessary for SSDD's hypothesis to work is that all matter be sentient (knowing its own temperature), can sense the temperature of every body surrounding it no matter the distance and can control how much energy it radiates by amplitude and direction.
The question of the finite speed limit on information (c) brings time into the question. Neither we nor all universe's matter SSDD believes to be alive and thinking, can perceive our surroundings in real time. There is always a passage of time and thus the temperature of a remote object whose temperature is changing due to some ongoing process, can NOT be known and there would be a 50/50 chance (ie, VERY close to a guarantee) that a colder object would inadvertently radiate to a hotter object and thus violate the First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy).
He has confused (and I'm being generous with that term) net heat transfer with absolute heat transfer. Rather than the scenario in which all items radiate per their temperature, in SSDD's universe, only hotter things radiate to colder, and - somehow - the amount of that radiation is throttled depending on the delta T. All that is necessary for SSDD's hypothesis to work is that all matter be sentient (knowing its own temperature), can sense the temperature of every body surrounding it no matter the distance and can control how much energy it radiates by amplitude and direction.
The question of the finite speed limit on information (c) brings time into the question. Neither we nor any of the universe's matter that SSDD believes to be alive and thinking, can perceive our surroundings in real time. There is always a passage of time and thus the temperature of a remote object whose temperature is changing due to some ongoing process, can NOT be known and there would be a 50/50 chance (ie, VERY close to a guarantee) that a colder object would inadvertently radiate to a hotter object and thus violate the First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy).
So lets see an observed, measured example of energy moving from a cool object to a warm object at ambient temperature. You guys claim it is happening as if the claims were true...surely you can provide observed, measured examples.
He has confused (and I'm being generous with that term) net heat transfer with absolute heat transfer. Rather than the scenario in which all items radiate per their temperature, in SSDD's universe, only hotter things radiate to colder, and - somehow - the amount of that radiation is throttled depending on the delta T. All that is necessary for SSDD's hypothesis to work is that all matter be sentient (knowing its own temperature), can sense the temperature of every body surrounding it no matter the distance and can control how much energy it radiates by amplitude and direction.
The question of the finite speed limit on information (c) brings time into the question. Neither we nor all universe's matter SSDD believes to be alive and thinking, can perceive our surroundings in real time. There is always a passage of time and thus the temperature of a remote object whose temperature is changing due to some ongoing process, can NOT be known and there would be a 50/50 chance (ie, VERY close to a guarantee) that a colder object would inadvertently radiate to a hotter object and thus violate the First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy).
So lets see an observed, measured example of energy moving from a cool object to a warm object at ambient temperature. You guys claim it is happening as if the claims were true...surely you can provide observed, measured examples.