- Mar 11, 2015
- 76,571
- 33,255
- 2,330
So we are told that if blacks do certain things that we will suceed.
1) Waiting until marriage to have children, and then only when at least one of the marriage partners is gainfully employed in a job that allows them to afford them, and
2) A very strong emphasis that education is the key to success - including higher education in a marketable field - that is instilled beginning in elementary school.
Of course, there are other traits that contribute to one’s degree of success - motivation, ability, intelligence, discipline, etc. - but the two above, if followed, practically guarantees that one will become at least lower-middle class, and likely higher.
Are these things relly how whites became sucessful?
Whether it was colonial government or the current republic we have now, the government has provided whites with more than it has ever given to anyone else. This was not because people of color did not take the opportunity because most of these things EXCLUDED non white participation. The handouts/privilege started with this:
In 1618, the Virginia colony passed "the Great Charter of privileges, orders, and laws." Among these laws was a provision that any person who settled in Virginia or paid for the transportation of another person to settle in Virginia would get fifty acres of land per person. “The right to receive fifty acres per person, or per head, was called a headright.” It got even better for colonists as those who “imported” slaves also got fifty acres per slave. The practice was continued by the government of Virginia, for 161 years, ending in 1779. Headrights were not only limited to Virginia. The headright system was used in all the original thirteen colonies. Headrights were the first of many government handouts of free stuff or guarantees providing whites with economic development assistance.
It continued with this:
The Three-Fifths Compromise is found in Article 1, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution. It says: “Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three-fifths of all other Persons.”
And with this:
The Naturalization Act of 1790 states: “any alien, being a free white person,” could apply for citizenship, so long as they lived in the United States for at least two years and in the state where the application was filed for at least one year. This law allowed “children of citizens of the United States that may be born … out of the limits of the United States shall be considered as natural-born citizens.” Please notice the first seven words. Only whites were entitled to be citizens of this country.
And with this:
One of the greatest miscarriages of justice in this nation’s history was a direct rebuttal to the claim that all men are created equal called Dred Scott v. Sandford. I am not going into all the particulars of this case. The court’s opinion says all you need to know. “A black man has no rights a white man is bound to respect.” The result of Dred Scott v. Sandford was that whites were given rights and status blacks were denied.Or- Affirmative Action.
And with this:
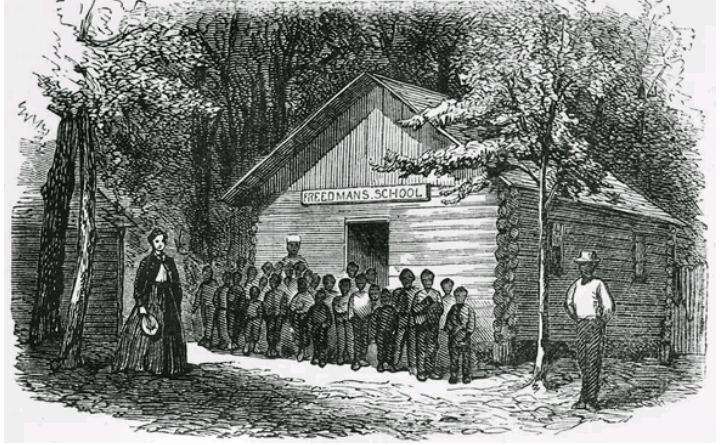
Anti-literacy Laws in the United States Once Prevented Blacks from Getting an Education
(NO OTHER RACE WAS DENIED THE RIGHT TO READ)
Passed in 1862, the Homestead Acts gave away 246 million acres of land. To qualify for Homestead land, a person had to be a citizen of the United States, and blacks were not given citizenship until 1866.
And this:
"After the Civil War ended in 1865, some states passed black codes that severely limited the rights of Black people, many of whom had been enslaved. These codes limited what jobs African Americans could hold, and their ability to leave a job once hired. Some states also restricted the kind of property Black people could own. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 weakened the effect of the Black codes by requiring all states to uphold equal protection under the 14th Amendment, particularly by enabling Black men to vote. (U.S. law prevented women of any race from voting in federal elections until 1920.)
During Reconstruction, many Black men participated in politics by voting and by holding office. Reconstruction officially ended in 1877, and southern states then enacted more discriminatory laws. Efforts to enforce white supremacy by legislation increased, and African Americans tried to assert their rights through legal challenges. However, this effort led to a disappointing result in 1896, when the Supreme Court ruled, in Plessy v. Ferguson, that so-called “separate but equal” facilities—including public transport and schools—were constitutional. From this time until the Civil Rights Act of 1964, discrimination and segregation were legal and enforceable."
July 9, 2018 was the 150th anniversary of the 14th Amendment, which purported to grant African Americans the rights and responsibilities of full citizenship, among other things. American history shows that people who are equal on paper can be unequal in practice—especially with regards to the right to bear arms.
On April 16, 1895, the United States Supreme Court rendered another one of the sorriest decisions in American history. It is known as Plessy vs. Ferguson. From this decision came the principle of separate but equal.
And this:
The National Housing Act was passed by Congress and signed by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1934.29 This law created the Federal Housing Administration or the FHA. The National Housing Act is the policy that may have had the most impact on wealth accumulation in modern America.
Between 1934 and 1968, the FHA implemented and put into practice a policy that still negatively impacts communities today.30 The FHA Underwriting Manual set the guidelines real estate agents used to assess home values in American neighborhoods. This manual promoted racist real estate practices. It was done by defending racially restrictive covenants and segregated communities. Due to this manual, the FHA established a neighborhood grading system based purely on false racist perceptions.
Redlining was the name of that grading system. My point here is the FHA was a government agency whose policies specifically provided whites with opportunities to increase wealth through homeownership. The formation of the FHA and its guaranteed loan program only worked to increase white advantage. “Of the $120 billion worth of new housing subsidized by the government between 1934 and 1962, less than 2 percent went to nonwhite families.”
"The racial-exclusion clauses in deeds were not only recommended by the federal government, but in some cases required as a condition of Federal Housing Administration and Veterans Administration subsidies for the creation of all-white suburbs, like Levittown in New York state. And federal and state courts, in violation of their constitutional obligations, enforced those deed clauses by ordering the eviction of African Americans who bought homes where the deeds barred them from doing so."
And this:
The Social Security Act of 1935 created the Social Security program, state unemployment insurance, and assistance to single women with children.Today, most Americans love the program. However, when the act was signed, the law excluded occupations mainly done by blacks. When President Roosevelt signed the law, approximately two-thirds of the blacks in America were ineligible. For years, most blacks were excluded from social security savings and could not get unemployment.
And this:
Title 4 or IV of the social security act of 1935 provided grants to states as Aid To Dependent Children. Eventually the name of the program was changed to Aid to Families with Dependent Children. This was welfare, folks. Assistance for single moms with children and no daddy at home. In 1935. Blacks were excluded.
And this:
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 created the minimum wage and time and a half overtime pay for working over forty hours a week. Child labor was eliminated by this act. All these were good things, but… In every law that was passed as part of The New Deal, Roosevelt had to compromise with southern representatives to get the votes he needed. In the case of the FLSA, due to pressure from southern congress members, he decided that industries would be excluded from the regulations where the majority of workers were black. Because of this, blacks were paid less than the minimum wage.
And this:
On June 22, 1944, President Roosevelt signed the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act, better known as the G.I. Bill.38 This law provided benefits for veterans returning from World War Two. This act included funds for college tuition, low-cost home loans, and unemployment insurance. As in every other program during this time, southern members of Congress fought the passage of these laws unless there were provisions that limited access to blacks.
Over one million returning black soldiers were unable to get GI benefits. My father was one of those soldiers.
Headrights, Headrights (VA-NOTES)
What was the Headright System? Headright System History & Significance | What was the Headright System? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Williams, T. (2000). The Homestead Act: A major asset-building policy in American history (CSD Working Paper No. 00-9). St. Louis, MO: Washington University, Center for Social Development. Pg.11 The Homestead Act: A Major Asset-Building Policy in American History
Freedmen's Bureau Act, Freedmen's Bureau Act, March 3, 1865 | The Freedmen's Bureau Online

 education.nationalgeographic.org
education.nationalgeographic.org

 www.topic.com
www.topic.com
James Chen, National Housing Act, Updated Sep 3, 2019, What Is the National Housing Act?
Alexis C. Madrigal, The Racist Housing Policy That Made Your Neighborhood, The Atlantic, May 22, 2014, The Racist Housing Policy That Made Your Neighborhood

 www.businessinsider.com
www.businessinsider.com
PBS, Race-The Power of An Illusion, Uncle Sam Lends A Hand, Did the Government Racialize Housing and Wealth? RACE - The Power of an Illusion . Go Deeper | PBS
The Social Security Act of 1935, Social Security History
Larry DeWitt, The Decision to Exclude Agricultural and Domestic Workers from the 1935 Social Security Act, Social Security Bulletin, Vol. 70, No. 4, 2010
Brad Plumer, A second look at Social Security’s racist origins, Washington Post, June 3, 2013, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news...cond-look-at-social-securitys-racist-origins/
Linda Gordon and Felice Batlan, The Legal History of the Aid to Dependent Children Program, Aid To Dependent Children: The Legal History
Johnathan Grossman, Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938: Maximum Struggle for a Minimum Wage, U.S. Department of Labor, Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938: Maximum Struggle for a Minimum Wage | U.S. Department of Labor
Servicemen’s Readjustment Act (G.I. Bill), Servicemen's Readjustment Act (1944) Facts - G.I. Bill for Veterans
Erin Blakemore, How the GI Bill's Promise Was Denied to a Million Black WWII Veterans, How the GI Bill's Promise Was Denied to a Million Black WWII Veterans, June 21, 2019
Brandon Weber, How African American WWII Veterans Were Scorned By the G.I. Bill, The Progressive, November 10, 2017, How African American WWII Veterans Were Scorned By the G.I. Bill
Sally Kohn, Affirmative Action Has Helped White Women More Than Anyone, Time, JUNE 17, 2013, Affirmative Action Has Helped White Women More Than Anyone.
Fact Sheet: Affirmative Action and What It Means for Women, July 1, 2000, The National Womens Law Center, https://nwlc.org/resources/affirmative-action-and-what-it-means-women/
Tim Wise, Is Sisterhood Conditional?: White Women and the Rollback of Affirmative Action, September 23, 1998, Is Sisterhood Conditional?: White Women and the Rollback of Affirmative Action
Victoria M. Massie, White women benefit most from affirmative action — and are among its fiercest opponents, White women benefit most from affirmative action — and are among its fiercest opponents
Do you really want blacks to emulate the actions of "more successful" groups?
1) Waiting until marriage to have children, and then only when at least one of the marriage partners is gainfully employed in a job that allows them to afford them, and
2) A very strong emphasis that education is the key to success - including higher education in a marketable field - that is instilled beginning in elementary school.
Of course, there are other traits that contribute to one’s degree of success - motivation, ability, intelligence, discipline, etc. - but the two above, if followed, practically guarantees that one will become at least lower-middle class, and likely higher.
Are these things relly how whites became sucessful?
Whether it was colonial government or the current republic we have now, the government has provided whites with more than it has ever given to anyone else. This was not because people of color did not take the opportunity because most of these things EXCLUDED non white participation. The handouts/privilege started with this:
In 1618, the Virginia colony passed "the Great Charter of privileges, orders, and laws." Among these laws was a provision that any person who settled in Virginia or paid for the transportation of another person to settle in Virginia would get fifty acres of land per person. “The right to receive fifty acres per person, or per head, was called a headright.” It got even better for colonists as those who “imported” slaves also got fifty acres per slave. The practice was continued by the government of Virginia, for 161 years, ending in 1779. Headrights were not only limited to Virginia. The headright system was used in all the original thirteen colonies. Headrights were the first of many government handouts of free stuff or guarantees providing whites with economic development assistance.
It continued with this:
The Three-Fifths Compromise is found in Article 1, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution. It says: “Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three-fifths of all other Persons.”
And with this:
The Naturalization Act of 1790 states: “any alien, being a free white person,” could apply for citizenship, so long as they lived in the United States for at least two years and in the state where the application was filed for at least one year. This law allowed “children of citizens of the United States that may be born … out of the limits of the United States shall be considered as natural-born citizens.” Please notice the first seven words. Only whites were entitled to be citizens of this country.
And with this:
One of the greatest miscarriages of justice in this nation’s history was a direct rebuttal to the claim that all men are created equal called Dred Scott v. Sandford. I am not going into all the particulars of this case. The court’s opinion says all you need to know. “A black man has no rights a white man is bound to respect.” The result of Dred Scott v. Sandford was that whites were given rights and status blacks were denied.Or- Affirmative Action.
And with this:
Anti-literacy Laws in the United States Once Prevented Blacks from Getting an Education
(NO OTHER RACE WAS DENIED THE RIGHT TO READ)
Passed in 1862, the Homestead Acts gave away 246 million acres of land. To qualify for Homestead land, a person had to be a citizen of the United States, and blacks were not given citizenship until 1866.
And this:
"After the Civil War ended in 1865, some states passed black codes that severely limited the rights of Black people, many of whom had been enslaved. These codes limited what jobs African Americans could hold, and their ability to leave a job once hired. Some states also restricted the kind of property Black people could own. The Reconstruction Act of 1867 weakened the effect of the Black codes by requiring all states to uphold equal protection under the 14th Amendment, particularly by enabling Black men to vote. (U.S. law prevented women of any race from voting in federal elections until 1920.)
During Reconstruction, many Black men participated in politics by voting and by holding office. Reconstruction officially ended in 1877, and southern states then enacted more discriminatory laws. Efforts to enforce white supremacy by legislation increased, and African Americans tried to assert their rights through legal challenges. However, this effort led to a disappointing result in 1896, when the Supreme Court ruled, in Plessy v. Ferguson, that so-called “separate but equal” facilities—including public transport and schools—were constitutional. From this time until the Civil Rights Act of 1964, discrimination and segregation were legal and enforceable."
July 9, 2018 was the 150th anniversary of the 14th Amendment, which purported to grant African Americans the rights and responsibilities of full citizenship, among other things. American history shows that people who are equal on paper can be unequal in practice—especially with regards to the right to bear arms.
On April 16, 1895, the United States Supreme Court rendered another one of the sorriest decisions in American history. It is known as Plessy vs. Ferguson. From this decision came the principle of separate but equal.
And this:
The National Housing Act was passed by Congress and signed by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1934.29 This law created the Federal Housing Administration or the FHA. The National Housing Act is the policy that may have had the most impact on wealth accumulation in modern America.
Between 1934 and 1968, the FHA implemented and put into practice a policy that still negatively impacts communities today.30 The FHA Underwriting Manual set the guidelines real estate agents used to assess home values in American neighborhoods. This manual promoted racist real estate practices. It was done by defending racially restrictive covenants and segregated communities. Due to this manual, the FHA established a neighborhood grading system based purely on false racist perceptions.
Redlining was the name of that grading system. My point here is the FHA was a government agency whose policies specifically provided whites with opportunities to increase wealth through homeownership. The formation of the FHA and its guaranteed loan program only worked to increase white advantage. “Of the $120 billion worth of new housing subsidized by the government between 1934 and 1962, less than 2 percent went to nonwhite families.”
"The racial-exclusion clauses in deeds were not only recommended by the federal government, but in some cases required as a condition of Federal Housing Administration and Veterans Administration subsidies for the creation of all-white suburbs, like Levittown in New York state. And federal and state courts, in violation of their constitutional obligations, enforced those deed clauses by ordering the eviction of African Americans who bought homes where the deeds barred them from doing so."
And this:
The Social Security Act of 1935 created the Social Security program, state unemployment insurance, and assistance to single women with children.Today, most Americans love the program. However, when the act was signed, the law excluded occupations mainly done by blacks. When President Roosevelt signed the law, approximately two-thirds of the blacks in America were ineligible. For years, most blacks were excluded from social security savings and could not get unemployment.
And this:
Title 4 or IV of the social security act of 1935 provided grants to states as Aid To Dependent Children. Eventually the name of the program was changed to Aid to Families with Dependent Children. This was welfare, folks. Assistance for single moms with children and no daddy at home. In 1935. Blacks were excluded.
And this:
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 created the minimum wage and time and a half overtime pay for working over forty hours a week. Child labor was eliminated by this act. All these were good things, but… In every law that was passed as part of The New Deal, Roosevelt had to compromise with southern representatives to get the votes he needed. In the case of the FLSA, due to pressure from southern congress members, he decided that industries would be excluded from the regulations where the majority of workers were black. Because of this, blacks were paid less than the minimum wage.
And this:
On June 22, 1944, President Roosevelt signed the Servicemen’s Readjustment Act, better known as the G.I. Bill.38 This law provided benefits for veterans returning from World War Two. This act included funds for college tuition, low-cost home loans, and unemployment insurance. As in every other program during this time, southern members of Congress fought the passage of these laws unless there were provisions that limited access to blacks.
Over one million returning black soldiers were unable to get GI benefits. My father was one of those soldiers.
Headrights, Headrights (VA-NOTES)
What was the Headright System? Headright System History & Significance | What was the Headright System? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
Williams, T. (2000). The Homestead Act: A major asset-building policy in American history (CSD Working Paper No. 00-9). St. Louis, MO: Washington University, Center for Social Development. Pg.11 The Homestead Act: A Major Asset-Building Policy in American History
Freedmen's Bureau Act, Freedmen's Bureau Act, March 3, 1865 | The Freedmen's Bureau Online

The Black Codes and Jim Crow Laws
After the United States Civil War, state governments that had been part of the Confederacy tried to limit the voting rights of Black citizens and prevent contact between Black and white citizens in public places.

The Unequal History of African American Gun Rights
When it comes to firearms, some Americans are more equal than others.
James Chen, National Housing Act, Updated Sep 3, 2019, What Is the National Housing Act?
Alexis C. Madrigal, The Racist Housing Policy That Made Your Neighborhood, The Atlantic, May 22, 2014, The Racist Housing Policy That Made Your Neighborhood
Segregation has been embraced, mandated, and maintained in the United States by law and policy — here's how
A conversation with author Richard Rothstein on the laws and policies that prevent Black and white Americans from living in integrated neighborhoods.
PBS, Race-The Power of An Illusion, Uncle Sam Lends A Hand, Did the Government Racialize Housing and Wealth? RACE - The Power of an Illusion . Go Deeper | PBS
The Social Security Act of 1935, Social Security History
Larry DeWitt, The Decision to Exclude Agricultural and Domestic Workers from the 1935 Social Security Act, Social Security Bulletin, Vol. 70, No. 4, 2010
Brad Plumer, A second look at Social Security’s racist origins, Washington Post, June 3, 2013, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news...cond-look-at-social-securitys-racist-origins/
Linda Gordon and Felice Batlan, The Legal History of the Aid to Dependent Children Program, Aid To Dependent Children: The Legal History
Johnathan Grossman, Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938: Maximum Struggle for a Minimum Wage, U.S. Department of Labor, Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938: Maximum Struggle for a Minimum Wage | U.S. Department of Labor
Servicemen’s Readjustment Act (G.I. Bill), Servicemen's Readjustment Act (1944) Facts - G.I. Bill for Veterans
Erin Blakemore, How the GI Bill's Promise Was Denied to a Million Black WWII Veterans, How the GI Bill's Promise Was Denied to a Million Black WWII Veterans, June 21, 2019
Brandon Weber, How African American WWII Veterans Were Scorned By the G.I. Bill, The Progressive, November 10, 2017, How African American WWII Veterans Were Scorned By the G.I. Bill
Sally Kohn, Affirmative Action Has Helped White Women More Than Anyone, Time, JUNE 17, 2013, Affirmative Action Has Helped White Women More Than Anyone.
Fact Sheet: Affirmative Action and What It Means for Women, July 1, 2000, The National Womens Law Center, https://nwlc.org/resources/affirmative-action-and-what-it-means-women/
Tim Wise, Is Sisterhood Conditional?: White Women and the Rollback of Affirmative Action, September 23, 1998, Is Sisterhood Conditional?: White Women and the Rollback of Affirmative Action
Victoria M. Massie, White women benefit most from affirmative action — and are among its fiercest opponents, White women benefit most from affirmative action — and are among its fiercest opponents
Do you really want blacks to emulate the actions of "more successful" groups?



