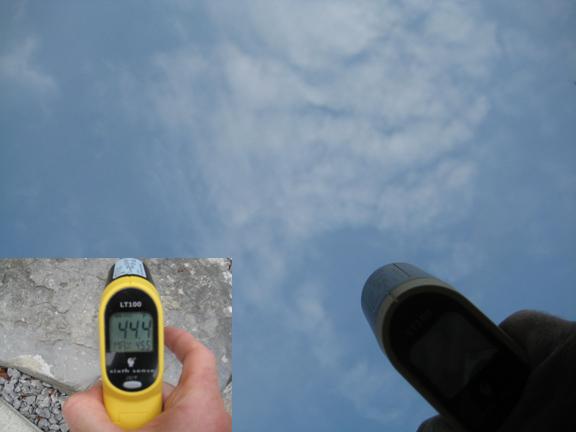
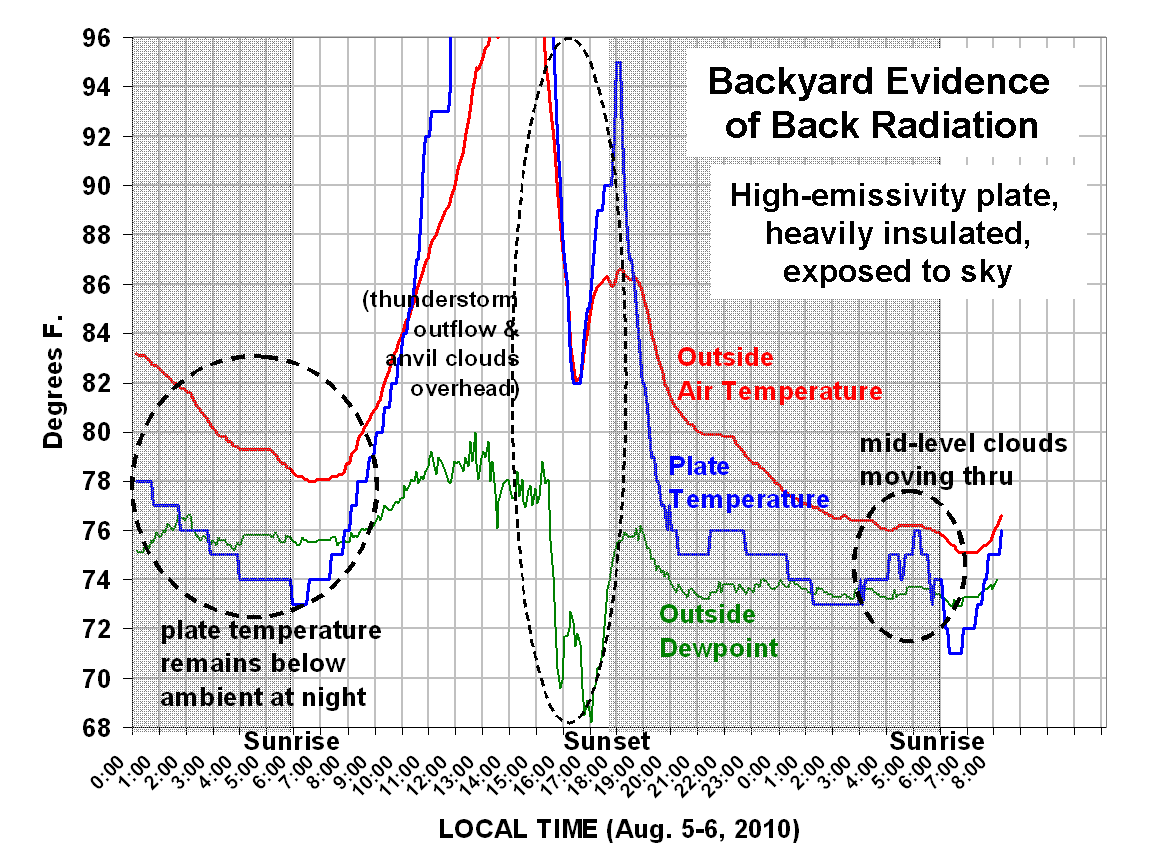
The sun warms the ground and the ground warms the air. That we can all agree on.
Heat can only be transferred from a warmer mass to a colder one, but the AGW advocates argue that heat can also be transferred from the colder mass to the warmer one. Climate "scientists" must insist on it else they don't have a case.
That means that the air has to be able to warm the warmer ground with "back radiation", which they say has increased with the increase in CO2.
They don't worry about mass or specific heat and simply apply black body physics for the radiative heat transfer while eyeballing heat conduction and convection yet claim that their results are accurate within a fraction of a degree.
Any scientist and/or engineer who has to deal with heat transfer in the real world knows how ridiculous this claim is.
Since 7/10 th of the earth surface is water and air at 400 ppm is available and free it is very easy to prove that
All it takes is 2 soda cans filled with water, one hot an another one cold, take note of the room temperature and observe the heat transfer.
Wait till the can with the warm water has cooled to 10 deg C above room temperature and note the time.
After 1 hour note the water temperature. Next measure the exact dimensions of the soda can and the amount of water in it. That allows you to get the cals per second or the # of watts.
The pop can surface area was 292.3 cm^2 the water in it was 370 ccm and it cooled from 34.5 C to 30 C in 1 hour. So it transferred 1665 calories (6996 watt sec) in 1 hour to the air that was 10.5 deg C cooler.
With the STB equation for this temperature difference you get 65 Watt/m^2
I observed 66.5 Watt/m^2 which of course includes heat conduction from the water through the thin Alu skin and into still air (convection=negligeble)....which are the extra 1.5 watt/m^2 (heat conduction) over the theoretical 65 W radiative transfer
If the climate warmers were right I should have only had 65(StB) - 1.8 (back radiation)+ my 1.5 conduction = 64.7 Watts/m^2
Which would be less cooling ergo more warming....but that did not happen, neither is global warming by CO2 back radiation.
Heat can only be transferred from a warmer mass to a colder one, but the AGW advocates argue that heat can also be transferred from the colder mass to the warmer one. Climate "scientists" must insist on it else they don't have a case.
That means that the air has to be able to warm the warmer ground with "back radiation", which they say has increased with the increase in CO2.
They don't worry about mass or specific heat and simply apply black body physics for the radiative heat transfer while eyeballing heat conduction and convection yet claim that their results are accurate within a fraction of a degree.
Any scientist and/or engineer who has to deal with heat transfer in the real world knows how ridiculous this claim is.
Since 7/10 th of the earth surface is water and air at 400 ppm is available and free it is very easy to prove that
All it takes is 2 soda cans filled with water, one hot an another one cold, take note of the room temperature and observe the heat transfer.
Wait till the can with the warm water has cooled to 10 deg C above room temperature and note the time.
After 1 hour note the water temperature. Next measure the exact dimensions of the soda can and the amount of water in it. That allows you to get the cals per second or the # of watts.
The pop can surface area was 292.3 cm^2 the water in it was 370 ccm and it cooled from 34.5 C to 30 C in 1 hour. So it transferred 1665 calories (6996 watt sec) in 1 hour to the air that was 10.5 deg C cooler.
With the STB equation for this temperature difference you get 65 Watt/m^2
I observed 66.5 Watt/m^2 which of course includes heat conduction from the water through the thin Alu skin and into still air (convection=negligeble)....which are the extra 1.5 watt/m^2 (heat conduction) over the theoretical 65 W radiative transfer
If the climate warmers were right I should have only had 65(StB) - 1.8 (back radiation)+ my 1.5 conduction = 64.7 Watts/m^2
Which would be less cooling ergo more warming....but that did not happen, neither is global warming by CO2 back radiation.
Last edited: