Old Rocks
Diamond Member
TC - Abstract - Area change of glaciers in the Canadian Rocky Mountains, 1919 to 2006
Area change of glaciers in the Canadian Rocky Mountains, 1919 to 2006
C. Tennant1, B. Menounos1,2, R. Wheate1,2, and J. J. Clague3
1Geography Program, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, British Columbia, V2N 4Z9, Canada
2Natural Resources and Environmental Studies Institute, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, British Columbia, V2N 4Z9, Canada
3Department of Earth Sciences, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia, V5A 1S6, Canada
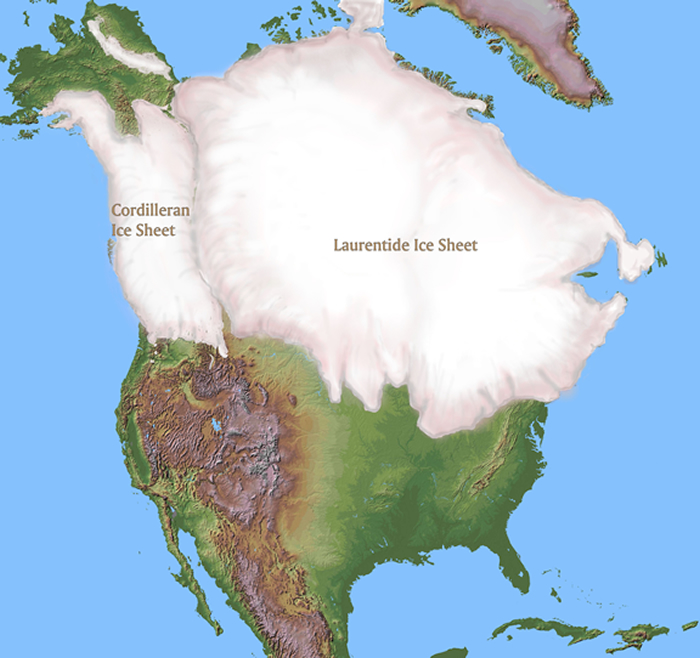
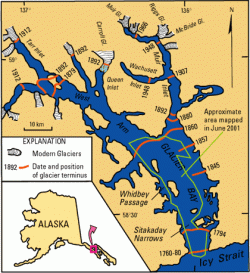
Abstract. Glaciers in the Canadian Rocky Mountains constitute an important freshwater resource. To enhance our understanding of the influence climate and local topography have on glacier area, large numbers of glaciers of different sizes and attributes need to be monitored over periods of many decades. We used Interprovincial Boundary Commission Survey (IBCS) maps of the AlbertaBritish Columbia (BC) border (19031924), BC Terrain Resource Information Management (TRIM) data (19821987), and Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) and Enhanced Thematic Mapper (ETM+) imagery (20002002 and 2006) to document planimetric changes in glacier cover in the central and southern Canadian Rocky Mountains between 1919 and 2006. Over this period, glacier cover in the study area decreased by 590 ± 70 km2 (40 ± 5%), 17 of 523 glaciers disappeared and 124 glaciers fragmented into multiple ice masses. Glaciers smaller than 1.0 km2 experienced the greatest relative area loss (64 ± 8%), and relative area loss is more variable with small glaciers, suggesting that the local topographic setting controls the response of these glaciers to climate change. Small glaciers with low slopes, low mean/median elevations, south to west aspects, and high insolation experienced the largest reduction in area. Similar rates of area change characterize the periods 19191985 and 19852001; −6.3 ± 0.6 km2 yr−1 (−0.4 ± 0.1% yr−1) and −5.0 ± 0.5 km2 yr−1 (−0.5 ± 0.1% yr−1), respectively. The rate of area loss, however, increased over the period 20012006; −19.3 ± 2.4 km2 yr−1 (−2.0 ± 0.2% yr−1). Applying size class-specific scaling factors, we estimate a total reduction in glacier cover in the central and southern Canadian Rocky Mountains for the period 19192006 of 750 km2 (30%).
Area change of glaciers in the Canadian Rocky Mountains, 1919 to 2006
C. Tennant1, B. Menounos1,2, R. Wheate1,2, and J. J. Clague3
1Geography Program, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, British Columbia, V2N 4Z9, Canada
2Natural Resources and Environmental Studies Institute, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, British Columbia, V2N 4Z9, Canada
3Department of Earth Sciences, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia, V5A 1S6, Canada
Abstract. Glaciers in the Canadian Rocky Mountains constitute an important freshwater resource. To enhance our understanding of the influence climate and local topography have on glacier area, large numbers of glaciers of different sizes and attributes need to be monitored over periods of many decades. We used Interprovincial Boundary Commission Survey (IBCS) maps of the AlbertaBritish Columbia (BC) border (19031924), BC Terrain Resource Information Management (TRIM) data (19821987), and Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) and Enhanced Thematic Mapper (ETM+) imagery (20002002 and 2006) to document planimetric changes in glacier cover in the central and southern Canadian Rocky Mountains between 1919 and 2006. Over this period, glacier cover in the study area decreased by 590 ± 70 km2 (40 ± 5%), 17 of 523 glaciers disappeared and 124 glaciers fragmented into multiple ice masses. Glaciers smaller than 1.0 km2 experienced the greatest relative area loss (64 ± 8%), and relative area loss is more variable with small glaciers, suggesting that the local topographic setting controls the response of these glaciers to climate change. Small glaciers with low slopes, low mean/median elevations, south to west aspects, and high insolation experienced the largest reduction in area. Similar rates of area change characterize the periods 19191985 and 19852001; −6.3 ± 0.6 km2 yr−1 (−0.4 ± 0.1% yr−1) and −5.0 ± 0.5 km2 yr−1 (−0.5 ± 0.1% yr−1), respectively. The rate of area loss, however, increased over the period 20012006; −19.3 ± 2.4 km2 yr−1 (−2.0 ± 0.2% yr−1). Applying size class-specific scaling factors, we estimate a total reduction in glacier cover in the central and southern Canadian Rocky Mountains for the period 19192006 of 750 km2 (30%).